70 |
Central Eastern Europe GRIP 2017
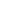
Triggered by the behaviour of Volkswagen in the US in 2015, it has recently come
under discussion whether new diesel cars reach the EURO 6 standards only under
laboratory conditions, while emitting much higher quantities of harmful substances
during normal operating conditions. This effect is even intensified when considering
that commercial vehicles in urban areas typically operate in a stop-and-go mode,
e. g. garbage collection trucks. In this low power range, the diesel engine is very
inefficient and emits more NO
x
and PM than in test driving cycles. According to a
study by DLR in 2013 (shown in Figure 5.11), the real NO
x
emissions exceeded the
limit while the EURO 5 standards were in force. A similar study by the International
Council on Clean Transportation in 2016 (given in Figures 5.12 and 5.13) also
suggests that passenger cars do not meet the EURO 6 standards under normal
operating conditions either. These facts put pressure on the manufacturers and may
lead to a tightening of EURO 6 for diesel, causing a further increase in the cost of
after-treatment. It should also be noted that diesel engines generally fulfil the
foreseen environmental requirements only in a narrow band of operating conditions
(especially with regard to ambient temperatures). By contrast, combustion engines
using NG fulfil all emissions requirements regardless of the NGVs´ operational mode,
speed, and load.
0
0.1
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.6
g/km
Limit 0.18
Diesel
CNG
0
0.1
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.6
g/km
Limit 0.08
Diesel
CNG
Figure 5.11:
Real NO
x
emission of a mid-sized passenger car
while EURO 5 was in force
(Source: DLR [Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und
Raumfahrt] & Partners [July 2013])
Figure 5.12:
Real NO
x
emission of a mid-sized passenger car
while EURO 6 is in force
(Source: DLR [Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und
Raumfahrt] & Partners [July 2013]) and
The International Council on Clean Transportation
[December 2016])
Figure 5.13:
Real NO
x
emissions of a heavy-duty diesel vehicle
and a passenger diesel vehicle
(Source: The International Council on Clean
Transportation [December 2016])
0
1.0
0.5
4.5
3.5
4.0
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
5.0
g/km
EURO V
EURO VI
EURO 6