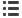
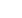
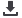
pH Measuring System
pH Electrode
The sensor half-cell of an electrochemical cell that is typically
composed of a special glass membrane that responds to hydrogen ion
concentration.
Reference Electrode
The half-cell of an electrochemical cell that supplies a stable
voltage that is known, constant, and completely insensitive to the
measurement solution. Changes in voltages generated from the pH
sensor are measured versus this electrode’s voltage.
High Input Impedance Meter
The measurement device that processes the voltage from the
electrochemical cell and converts it into a meaningful measurement
unit (pH). The measurement is done with virtually zero current flow
to prevent polarization of the electrodes. Modern pH meters also may
provide sensor diagnostics, automatic buffer recognition, calibration
reminders and user prompts.
Chemical pH Buffers
Stable, well-characterized standards used for calibration. Two or more
pH buffers that bracket the sample pH range are suggested for the
most accurate results.
Thermometer or Temperature Probe
A temperature measurement is desired during calibration and
measurement to make adjustments to the Nernst slope factor. An
auxiliary or built-in temperature probe ensures both calibration and
measurement are automatically temperature compensated, thus
eliminating error.
Magnetic Stirrer
Used in a laboratory setting, amagnetic stirrer together withmagnetic
stir bars continually agitate the buffer and/or samples to keep them
homogenous, eliminating temperature or sample gradients.
Electrode Design
Ag/AgCl Internal
Wire
Buffered KCl
Solution
pH Sensitive
Glass
Internal Reference
Wire
High Concentration
Electrolyte Solution
(i.e. 3.5M KCl and
AgCl Electrolyte)
Salt Bridge Junction
Connecting the
Reference to the
External Solution
pH Half-cell
Reference
Half-cell
Ag/AgCl
Reference Wire
Ceramic Junction
Combination pH
Electrode
Inner Tube Housing
the Membrane Sensing
Wire
Electrolyte
Containing Silver
Half-cells vs. Combination pH electrodes
Until the 1970s, it was a common practice to offer two half cells
separately, aglass pHsensor anda referenceelectrode. Today it ismore
common to use a single combined electrode that has both sensing and
reference components. Reference electrodes still enjoy use in other
electrochemical techniques and their use is often preferred with ion
selective electrodes (ISE) half-cells.
pH Electrodes
Designed and Manufactured by Hanna
2
pH
2.100
|
www.hannainst.comelectrodes