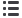
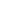
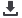
Economic
Vulnerability
Weight - 60%
Social
Vulnerability
Weight - 20%
Environmental
Vulnerability
Weight - 20%
Risk of Harm
The risk of an economy being
harmed is the difference between its
vulnerability and resilience
Export Concentration (20%)
Measures a country’s reliance on a fewmajor
exports and on a few key export trading
partners
Dependence on Strategic Imports (20%)
Measures a country’s dependence on critical
imported goods (food and energy) to meet
domestic consumption and production
Dependence on Foreign Capital (20%)
Measures a country’s reliance on external
sources of capital to achieve its development
objectives
Social Susceptibility (20%)
Measures the social vulnerability of a country
through health, education, gender equality,
poverty, and crime
Natural Hazards & Climate Change (20%)
Measures a country’s susceptibility to natural
hazards and climate change
Macroeconomic
Stability
Weight - 60%
Social Security
and Good
Governance
Weight - 20%
Environmental
Preparedness
Weight - 20%
Measures a country’s ability to foster
sustained growth and respond to economic
shocks through foreign exchange buffers,
prudent fiscal policy, and manageable debt
levels
Measures a country’s ability to promote social
cohesion and good governance
Measures a country’s ability to withstand and
respond to natural disasters
Vulnerability Index
Resilience Index
At CDB, we are exploring the possibility of using the vulnerability and
resilience index to improve BMCs access to concessional financing