24
1
The Basics
2.
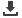
Anterior fascicle
, which runs along the anterior wall of the left
ventricle
3.
Posterior fascicle
, which sweeps over the posterior wall of the left
ventricle
The right bundle branch and the left bundle branch and its
fascicles terminate in countless tiny Purkinje fibers, which resemble
little twigs coming off the branches of a tree. These fibers deliver
the electrical current into the ventricular myocardium.
Ventricular myocardial depolarization causes ventricular
contraction. It is marked by a large deflection on the EKG called the
QRS complex
. The amplitude of the QRS complex is much greater
than that of the atrial P wave because the ventricles have so much
more muscle mass than the atria. The QRS complex is also more
complicated and variable in shape than the P wave, reflecting the
greater intricacy of the pathway of ventricular depolarization.
Left
posterior
fascicle
Right bundle branch
Purkinje fibers
Left anterior fascicle
Septal fascicle
Left bundle branch
Bundle of His
AV node
The ventricular conduction system, shown in detail. Below the bundle
of His, the conduction system divides into right and left bundle
branches. The right bundle branch remains intact, whereas the left
divides into three separate fascicles.