Bacterial repopulation after surgery & antibiotics
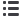
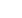
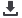
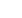
FIGURE 4.
PCoA of microbial communities. PCoA was performed on genus-level microbiome data using Morisita-Horn similarity scores calculated on each
pair of samples. The top 3 plots show the distribution of samples along PC1-PC2, PC1-PC3, and PC2-PC3. Baseline, 2-week, and 6-week samples are designated
by circles, squares, and triangles, respectively. Each subject is designated by a unique color. The bottom 12 plots display the PC1-PC2 plots for individual
subjects. ESS
=
endoscopic sinus surgery; PCoA
=
principal coordinates analysis.
complex interplay between the microbiome and therapeu-
tic interventions.
Conclusion
Bacterial communities colonizing the ethmoid at 6 weeks
postoperatively were most similar to anterior nasal cavity
and pretreatment sinus microbial profiles, indicating the
resilience of these sites and suggesting they may be poten-
tial sources for repopulation of bacteria postoperatively.
Bacterial communities appear to largely return to their nor-
mal preoperative state, with some degree of interpersonal
variation, identifying another variable that could affect
therapeutic outcomes. Interestingly, postoperative antibi-
otic therapy did not reduce the bacterial burden, but rather
shifted the microbial consortia.
References
1. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. European Posi-
tion Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012.
Rhinol Suppl
. 2012;(23):3 p preceding table of con-
tents, 1–298.
2. Giger, R, Dulguerov, P, Quinodoz, D, et al. Chronic
panrhinosinusitis without nasal polyps: long-term out-
come after functional endoscopic sinus surgery.
Oto-
laryngol Head Neck Surg
. 2004;131:534–541.
3. Lund, VJ. Evidence-based surgery in chronic rhinosi-
nusitis.
Acta Otolaryngol
. 2001;121:5–9.
4. Kennedy, DW. Prognostic factors, outcomes and
staging in ethmoid sinus surgery.
Laryngoscope
.
1992;102:1–18.
5. Smith, TL, Litvack, JR, Hwang, PH, et al.
Determinants of outcomes of sinus surgery: a
multi-institutional prospective cohort study.
Oto-
laryngol Head Neck Surg
. 2010;142:55–63.
6. Tan NC, Foreman A, Jardeleza C, Douglas R, Tran
H, Wormald PJ. The multiplicity of
Staphylococcus
aureus
in chronic rhinosinusitis: correlating surface
biofilm and intracellular residence.
Laryngoscope
.
2012;122:1655–1660.
International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, Vol. 6, No. 1, January 2016
125