87
ACCESSIBILITY TO FOOD
Accessibility to food concerns both physical access and af-
fordability. Access to markets concerns transportation of
commodities and its costs as well as the transmission of
price developments to producers. Poor transmission of
price incentives to producers results in broadening the gap
between consumers and producers, especially in periods
of changing diets.
ACCESS TO MARKETS
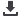
According to the latest UN estimates, almost all of the
world’s population growth between 2000 and 2030 will be
concentrated in urban areas in developing countries (Fig-
ure 32). By 2030, almost 60% of the people in developing
countries will live in cities (FAO, 2003). If present trends
continue, urban population will equal rural population by
around 2017.
Large urban markets create the scope for the establishment of big
supermarket chains, with implications for the entire food supply
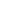
chain. In 2002, the share of supermarkets in the processed/pack-
aged food retail market was 33% in Southeast Asia and 63% in East
Asia (Figure 33). The share of supermarkets in the fresh foods mar-
ket was roughly 15–20% in Southeast Asia and 30% in East Asia
outside of China. The 2001 supermarket share of Chinese urban
food markets was 48%, up from 30% in 1999. Supermarkets are
also becoming an emerging force in South Asia, particularly in ur-
ban India since the mid-1990s (Pingali and Khwaja, 2004).
The increasing growth and power of international food corporations
are affecting the opportunities of small agricultural producers in de-
veloping countries. While new opportunities are being created, the
majority are not able to utilize them because of the stringent safety
and quality standards of food retailers, hence barring market entry.
The economy of the corporate food supply chain has grown steadily
over the past years. Between 2004 and 2006 total global food spend-
Urban and rural population
in less developed regions (billions)
1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030
0
1
2
3
4
Rural
Projections
Estimates
Urban
Figure 32: Urbanization in developing countries be-
tween 1960 and 2030.
(Source: UN, 2007).
Supermarket share of retail food sales
Central America
Southeast Asia
Central Europe
Kenya
Zimbabwe
South America
East Asia
(excl. China)
South Africa
China (urban)
0
10
20
30
40
50
1992
2002
Figure 33: Supermarket share of retail food sales.
(Source: Reardon
et al
., 2003).