significant bandwidth to execute
other important tasks. Protection
features, such as undervoltage
lockout (UVLO), overvoltage lockout
(OVLO) and output overvoltage
protection (OOVP) can be executed
by processing the sensed input and
output voltage. This ensures that
the LED driver is operating within
desired specifications and the LED
is protected from abnormal input
and output conditions. The CPU
can also process the thermal data
from a sensor to implement a LED’s
thermal management. Moreover,
when setting the dimming level
of the LED driver, the CPU can
process triggers from a simple
external switch or command from
a serial communication. Also, the
parameters of LED driver can be
sent to external devices through the
serial communication for monitoring
or testing.
Aside from the features mentioned
above, the designer has the luxury
to add more intelligence on their
own LED application inclusive
of communications, like DALI or
DMX, and control customizations.
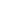
Figure 4 shows an example of a
complete switched-mode dimmable
LED driver solution using the LED
dimming engine.
Conclusion
A LED dimming engine can be used
to create an effective switched-
mode dimmable LED driver. The
effectivity equates on its capabilities
to drive multiple LED strings, to
provide efficient energy source, to
ensure LED’s optimal performance,
to maintain a long life for the LEDs
and to add intelligence in the
system.
Automotive
Special Edition
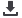
Figure 3. LED dimming waveform
Figure 4. Switched-mode dimmable LED driver solution
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 39