RISK FACTORS
04
4.1 Risk management and coverage
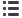
AREVA BUSINESS RISK MAPPING PROCESS SINCE JANUARY 2016
(1)
AREVA NP
ExCom
Source: AREVA.
Audit and Ethics Committee
CEO
Risk Committee
Risk and Internal
Audit Department
NewCo
ExCom
NewCo
Business Units
NewCo
Corporate Functions
AREVA NP
Business Units
AREVA NP
Corporate Functions
Validation of “Top risks”
proposed by the ExComs
of the NewCo and NP sub-groups
and reviewed by the Risk Committee
Coordination & follow-up
Guidelines
Review of “Top risks”
Leadership of the process
Addition of residual risks
specific to AREVA SA
and Group summary
Bottom
Up
Top
down
The first stage of the risk management process is to identify the risk using a Business Risk Model (BRM) drawn up for the use of the operating units. Working from a
defined number of typical risks or families of risk (BRM risk), the model lists all of the foreseeable or fortuitous situations or events which may have an impact on employee
safety, on the financial performance of the business unit, of the subgroup or even of the group, as well as on its corporate image.
The BRM evolves by incorporating best practices and lessons learned.
(1) For the 2015 mapping process, see the 2015 Reference Document, Section 4.1.1.
The establishment of the risk map is the time for collecting recommendations
and decision-making components concerning the implementation of action
plans designed to optimize the management of each risk and render the residual
risk acceptable to the group. The operating units are responsible for identifying,
analyzing and prioritizing their risks, and for managing themby implementing action
plans using appropriate means.
In each business unit, the riskmanagement coordinators provide their management
with a cross-business picture of risks and of how the sites and entities are managing
them. The Risk Committee is then informed of the status of action plans and decides
which risks affect the group’s strategic objectives.
The group’s commitment to transparency in riskmanagement is shown in particular
through the publication of environmental monitoring results for the principal sites
and more generally through the implementation of its Nuclear Safety Charter. A
measurement and reporting protocol frames the calculation and measurement of
sustainable development indicators published by the group.
The operating units, supported by AREVA’s specialized departments, manage risks
related to nuclear safety, the environment and the physical protection of AREVA’s
facilities, under the regulatory oversight of national and international authorities.
RISK MANAGEMENT RELATED TO THE GROUP’S INDUSTRIAL
OPERATIONS
In terms of regulation, industrial facilities operated by AREVA are categorized by
level of risk and the quantity of nuclear material or chemical substances present.
In addition to the means of preventing and countering acts of malfeasance and
actions to ensure public safety in the event of an accident, the industrial safety of
the facilities consists in particular of:
p
protecting employees, members of the public and the environment from the
harmful effects of radiation and chemicals; and
p
defining and implementing measures designed to prevent accidents and limit
their impacts.
12
2016 AREVA
REFERENCE DOCUMENT