BUSINESS OVERVIEW
06
6.1 Markets for nuclear power and renewable energies
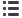
WORLD ELECTRIC POWER GENERATION IN 2014
16%
Hydraulic
11%
Nuclear
4%
Oil
41%
Coal
6%
Renewable energy
22%
Gas
Source: IEA,WEO 2016.
6.1.1.2.
NUCLEAR ENERGY
Nuclear power offers many advantages on the environmental, economic, strategic
and operational levels:
p
it helps combat climate change;
p
it creates significant added value locally as well as a large number of highly
qualified jobs that cannot be delocalized;
p
it is competitive compared with other sources of baseload electricity;
p
it offers stable production costs with less uncertainty concerning the price of
the electricity produced;
p
it ensures security of supply: nuclear fuel is easy to store and uranium resources
are well distributed around the world, unlike oil and gas reserves, which are
concentrated in Russia and the Middle East;
p
it is a solution for limiting trade deficits for countries that import fossil energies,
and it preserves the reserves of exporting countries by limiting their domestic use;
p
it offers heightened operational and safety performance, particularly with the
new generation III reactors developed by AREVA, the EPR and ATMEA1
reactors
(1)
.
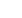
Nuclear power helps combat climate change
Nuclear power is already making a strong contribution to the fight against climate
change. The figure below shows that greenhouse gas emissions from nuclear
power are as low as those from renewable energies.
(1) The ATMEA1 reactor is being developed in collaboration with Mitsubishi Heavy Industry.
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS (GHG) BY POWER GENERATION SOURCE ACROSS THE ENTIRE OPERATING CYCLE
0
200
400
600
800
1,000
Biomass
Solar PV
Solar CSP
Geothermal energy
Hydraulic
Marine energy
Wind
Nuclear
Natural Gas
Coal
kg CO
2
eq/MWh
Source: IPCC, literature review, 2014.
46
2016 AREVA
REFERENCE DOCUMENT