example, societies are developing online training courses
for education and certification for APCs in
otolaryngology.
10
The role of APCs in providing outpatient care in
multiple different surgical disciplines, including otolar-
yngology, has been studied, particularly in countries
with national health services. For example, patient satis-
faction surveys have been conducted in Great Britain
regarding NPs in management of snoring and aural
care, among other conditions. Generally, care rendered
by these APCs has been viewed as good or very good in
these settings.
11,12
Similar data suggest that patients
are satisfied with the care offered by surgical nurse
practitioners in the Veterans Health Administration.
13
As the penetration of physician assistants in otolaryngol-
ogy remains limited, there are limited data regarding
patient satisfaction with visits incorporating PAs in oto-
laryngology. This is likely an area warranting future
research.
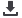
The current data provide a national estimate of
the type of care being provided by APCs and RNs in
outpatient, ambulatory, otolaryngology practices. A sub-
stantial fraction (25.1%) of ambulatory patients are
coming in contact with a nurse during their outpatient
otolaryngology visit. Nurses may provide a broad spec-
trum of care, including assistance with cerumen
removal, patient education, and allergy testing, among
others. However, because visits provided by nurses alone
are not typically subject to billing for clinical services, it
is not surprising that almost all visits in which a nurse
was involved also had a corresponding physician-pro-
vider component (Fig. 1). This lends to the validity of
the current data.
Currently, a relative minority of otolaryngologic
office visits are provided for by APCs, currently standing
at only 6.3%. When APC care was involved, NPs were
significantly more likely to see patients independent of a
physician during the office visit relative to care provided
by a PA. The greater fraction of independent NP care is
to be expected given that NPs are governed by the state
boards of nursing, and correspondingly, may be allowed
a greater degree of autonomy than PAs.
3
In some states,
NPs may be able to practice completely independently
(i.e., without collaboration) of a physician for diagnosis
and treatment.
2
In contrast, PA training and education
are strongly geared toward physician collaboration, and
TABLE II.
Top 10 Diagnosis Codes Seen by Physician Assistants and Nurse Practitioners.
PA
NP
Diagnosis
No.
Diagnosis
No.
(381) Nonsuppurative otitis media and
. . .
223,440
(380) Disorders of external ear
85,981
(380) Disorders of external ear
140,130
(474) Chronic disease of tonsils and
. . .
56,589
(784) Symptoms involving head and neck
110,734
(784) Symptoms involving head and neck
35,071
(706) Diseases of sebaceous glands
100,332
(530) Diseases of esophagus
32,387
(780) General symptoms
96,839
(995) Certain adverse effects, not el
. . .
32,387
(472) Chronic pharyngitis and nasopha
. . .
89,491
(V67) Follow-up examination
32,387
(701) Other hypertrophic and atrophic
. . .
63,366
(382) Suppurative and unspecified oti
. . .
26,797
(781) Symptoms involving nervous and
. . .
36,366
(477) Allergic rhinitis
26,797
(785) Symptoms involving cardiovascul
. . .
63,366
(462) Acute pharyngitis
18,863
(473) Chronic sinusitis
61,521
(472) Chronic pharyngitis and nasopha
. . .
18,863
PA
¼
physician assistant; NP
¼
nurse practitioner.
TABLE III.
Top 10 Diagnosis Codes Seen by Nurses and Physicians.
RN
MD Alone
Diagnosis
No.
Diagnosis
No.
(381) Nonsuppurative otitis media and
. . .
795,353
(380) Disorders of external ear
2,513,272
(380) Disorders of external ear
766,185
(381) Nonsuppurative otitis media and
. . .
1,938,697
(382) Suppurative and unspecified oti
. . .
615,322
(473) Chronic sinusitis
1,694,074
(784) Symptoms involving head and neck
493,870
(784) Symptoms involving head and neck
1,478,966
(473) Chronic sinusitis
491,677
(477) Allergic rhinitis
1,438,415
(389) Deafness
474,400
(382) Suppurative and unspecified oti
. . .
1,430,729
(477) Allergic rhinitis
361,161
(389) Deafness
1,306,010
(474) Chronic disease of tonsils and
. . .
349,586
(478) Other diseases of upper respira
. . .
1,033,903
(388) Other disorders of ear
331,049
(388) Other disorders of ear
884,837
(478) Other diseases of upper respira
. . .
316,126
(V67) Follow-up examination
844,266
RN
¼
registered nurse; MD
¼
medical doctor.
Laryngoscope 122: May 2012
Bhattacharyya: Physician Extenders in Otolaryngology
137