57
Coastal pollution and dead zones, disrupted food chains
Increased vulnerability of infestations by invasive species
Climate change
Die-off of cold water
corals with acidification
Less cold-water driven
flushing and reduced
nutrient flows
Further increase in dead zones
Further infestations on dead corals and in fishing grounds,
breakdown by wave activity and storms
Concentrated cumulative impacts in the primary fishing grounds
resulting in collapse or greatly reduced recovery rates
80-100% tropical coral
reef die-off from bleaching
Overharvest from fisheries
Habitat loss related to
coastal development
Damage to ocean beds from
bottom trawling
Shifts in marine life distributions and reduced
ocean productivity
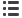
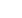
Figure 31. Climate change may,
inter alia
through effects on ocean currents, elevated sea temperatures, coral bleaching,
shifts in marine life, ocean acidification, severely exacerbate the combined impacts of accelerating coastal development
and pollution, dead zones, invasive species, bottom trawling and over-harvest.
These impacts will be the strongest in
10–15% of the World’s oceans, which harbour the most productive fishing grounds today, responsible for more than half
of the marine landings globally.