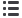
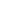
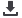
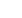
INV-assessed PFS by chemotherapy
backbone (10 September 2016 cut-off)
Hiddemann W, et al. ICML 2017 (Abstract 107)
HR, 0.68 (95% CI: 0.54, 0.87); p=0.0016
3-year PFS
:
81.5% for G-Chemo vs 75.0% for R-chemo
HR, 0.63 (95% CI: 0.46, 0.88); p=0.0062
3-year PFS
:
84.1% for G-B vs 76.4% for R-B
HR, 0.72 (95% CI: 0.48, 1.10); p=0.1266
3-year PFS
:
80.6% for G-CHOP vs 75.6% for R-CHOP
HR, 0.79 (95% CI: 0.42, 1.47); p=0.4560
3-year PFS
:
71.3% for G-CVP vs 64.2% for R-CVP
R-chemo
G-chemo
R-chemo
G-chemo
R-chemo
G-chemo
R-chemo
G-chemo
No. at risk
438
478
267
291
77
85
1
505
535
601
601
Time (months)
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1.0
Survival Probability
24 36 48 60
12
0
All patients
No. at risk
250
276
163
179
52
61
285
305
341
345
Time (months)
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1.0
Survival Probability
24 36 48 60
12
0
Bendamustine
No. at risk
152
153
84
84
20
18
1
179
174
203
196
Time (months)
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1.0
Survival Probability
24 36 48 60
12
0
CHOP
No. at risk
36
49
20
28
5
6
41
56
57
60
Time (months)
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1.0
Survival Probability
24 36 48 60
12
0
CVP
•
PFS was superior with G-chemo relative to R-chemo with consistent effects across chemo regimens
•
Study not designed or powered to compare differences between R-chemo and G-chemo within chemo groups