speech: nasality, nasal emission, facial grimace, phonatory characteris-
tics, and compensatory misarticulations (Table 1).
20
The complete PWSS
assessments as evaluated by the speech pathologists at every visit, were
reviewed. A lower PWSS denotes better speech than a higher PWSS.
Patients underwent OSA screening and counseling regarding signs/
symptoms at initial evaluation. Clinical suspicion (ie, breath-holding spells,
snoring) warranted further evaluation including diagnostic sleep stud-
ies. After surgical intervention, parents were questioned and counseled
at every postoperative visit regarding the persistence or development of
OSA. Further diagnostic studies were ordered as warranted.
Clinical indications for PPF takedown included: (1) OSA, (2) OSA
and deterioration of speech (ie, worsening PWSS), (3) borderline ade-
quate speech and possible midface advancement with or without OSA,
and/or (4) recurrent VPI and possible conversion Furlow palatoplasty.
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed with unpaired, 2-tailed
t
tests with a signifi-
cance level of
P
less than 0.05 using Prism GraphPad 5.0 (GraphPad
Software, Inc., La Jolla, Calif.) statistical software.
RESULTS
Sixty-four patients with a history of VPI who underwent PPF
takedown were identified during a 20-year period from 1992 to 2012.
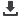
Forty-two patients (65.6%) underwent PPF takedown for OSA, 5
(7.8%) for OSA and deterioration of speech, 8 (12.5%) for borderline
adequate speech and possible midface advancement with or without
OSA, and 9 (14.1%) for recurrent VPI and possible conversion Furlow
palatoplasty (Fig. 1). All PPFs were in place for greater than 5 years
before takedown.
Thirty-seven patients (57.8%) were men. Eighteen patients
(28.1%) underwent PPF takedown alone, and 46 patients (71.9%)
underwent PPF takedown with conversion to Furlow palatoplasty.
Mean length of postoperative follow-up period was 38.1 ± 27.8 months
(range 1
–
104). Mean age at time of intervention was 12.4 ± 3.9 years
(3
–
22). Mean age for patients undergoing PFF takedown with con-
version to Furlow palatoplasty was 12.3 ± 3.9 years (3-20) compared
to 12.8 ± 4.2 years (7
–
22) for those undergoing PPF takedown
alone (
P
= 0.63).
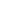
For all patients, mean preoperative PWSS was 5.7 ± 6.6 (range,
0
–
26) compared to 3.4 ± 4.5 (range, 0
–
27) after PPF takedown. No
statistically significant regression in PWSS occurred after PPF take-
down (
P
< 0.05). For patients undergoing PPF takedown alone, mean
preoperative (3.8 ± 6.1 [range, 0
–
23]) and postoperative PWSS
(4.1 ± 5.3 [range, 0
–
23]) were not significantly different (
P
= 0.89)
TABLE 1.
Pittsburgh Weighted Speech Score
Nasal Emission (0
–
3, Highest Value)
Right
Left
Not present
0
0
Inconsistent, visible
1
1
Consistent, visible
2
2
Audible
3
3
Turbulent
3
3
Facial Grimace (0/2, Presenc
e)
2
Nasality (0
–
4, Highest Value
)
Normal
0
Mild hypernasality
1
Moderate hypernasality
23
Severe hypernasality
4
Hypo-/hypernasality
2
Cul de sac
2
Hyponasality
0
Phonation (0
–
3, Highest Value
)
Normal
0
Mild hoarseness/breathiness
1
Moderate hoarseness/breathiness
2
Severe hoarseness/breathiness
3
Reduced loudness
2
Tension in system
3
Articulation (0
–
23, Summative
)
Normal
0
Developmental errors
0
Errors not related to VPI
0
Errors related to dentition
0
Reduced intraoral pressure from sibilants
1
Reduced intraoral pressure for fricatives
2
Reduced intraoral pressure for plosives
3
Omission of fricatives or plosives
2
Omission of fricatives or plosives plus hard glottal attack
for vowels
3
Lingual-palatal sibilants
2
Pharyngeal fricatives or plosives,
“
backing
”
, snorting,
inhalation or exhalation substitutions
3
Glottal stops
3
Nasal substitutions for pressure sounds
4
FIGURE 1.
Clinical indications for PPF takedown are obstructive
sleep apnea (black), obstructive sleep apnea with deterioration
of speech (dark grey), borderline adequate speech and the plan
for midface advancement with or without OSA (light grey), and
recurrent VPI with plans for conversion to Furlow
palatoplasty (white).
FIGURE 2.
Pittsburgh weighted speech scores pre-takedown
(black) and post-takedown (white) for all patients, PPF
takedown with conversion to Furlow palatoplasty, and PPF
takedown alone. All figures denote means with error bars
reflecting standard error of the mean.
**
represents a
P
value less
than 0.01 and
*
represents a
P
value less than 0.05.
Annals of Plastic Surgery
•
Volume 77, Number 4, October 2016
Speech Outcomes After PPF Takedown
© 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.annalsplasticsurgery.com42