13
environment, food security and disaster mitigation. It also ad-
dresses the key financial benefits involved in conservation, eco-
system restoration or ultimate loss of ecosystems and their role
in sustainable development. This includes not only the com-
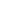
Figure 2:
Ecosystem connectivity and impacts on ecosystem services from human activities.
plexities of ecological restoration, but also the importance of
integrating the multistaker community involved, influencing
and influenced by the initial degradation and in the benefits of
restoration (Brander
et al
., 2006; Granek
et al
., 2010).
Y Y Y Y
YY
Y Y YYYYYYYYYYY
Y
Y Y
Y
Y
Coral reef
Offshore
waters
Seagrasses
Mangroves
Land
Decreased storm
buffering
Export of fish
and invertebrate
larvae and adults
Binding sediments
Absorb inorganic
nutrients
Binding sediments
Absorb inorganic
nutrients
Slow freshwater
discharge
Sediments
Habitat destruction
Changes in nutrients, sediments
and freshwater outputs
Loss of mangrove
and seagrass
habitat
Socio-economic
changes for coastal
populations
Increased sedimentation
and nutrient imput
Decreased fisheries, decreased
revenues from tourism, and
decreased storm buffering
Loss of coral reef habitat
Nutrients
Freshwater
discharge
Decreased storm
buffering and increased
coastal erosion
Export of
invertebrate and
fish larvae
Fish and invertebrate
habitat (adult
migration)
Storm buffering
Storm buffering
Fish and
invertebrate
habitat
Export of organic
material and
nutrients for nearshore
and offshore food webs
Export of organic
material and nutrients
for nearshore and
offshore food webs
Export of
invertebrate and
fish larvae
Fish and invertebrate
habitat (adult
migration)
Ecosystem connectivity and impacts on ecosystem services from human activities
Source: WCMC,
Framing the Flow,
2010.
Impacts
Ecosystem
connectivity