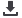
Fig: ARINC 653 compliant OS architecture
iii)
The historical dominance of
PowerPC in the embedded market
appears to be somewhat in decline,
and the long term future appears
to be uncertain with NXP (formerly
Freescale) developing ARM-based
processors as well as to PowerPC. In
addition, the large number of PowerPC
QorIQ processor architecture variants
makes it unclear if there will be a de
facto choice for avionics.
iv)
The increasing performance
of ARM-based processors means that
they may be considered as a viable
option for some types of avionics
application where PowerPC processors
had been used previously.
v)
Intel
processors
which
historically were not widely considered
for use in avionics applications due
in part to their power dissipation
requirements are now being
considered due to Intel’s low-power
14nm processor devices [3].
These market dynamics have resulted
in fragmentation of processor
selection for avionics, resulting in a
lack of an obvious, single successor
for widely-deployed PowerPC single
core processors. We are now facing
a wide range of contenders in terms
of ARM multi-core, PowerPC QorIQ
architecture families and Intel Core
and Atom architectures.
The Challenge of RTOS
Safety Certification
Undertaking DO-178B and ED-12B
Level A software certification of an
RTOS is extremely expensive, costing
millions of Euros and is specific to an
underlying processor architecture.
It is cost-prohibitive COTS real-time
operating system (RTOS) suppliers
to undertake DO-178B and ED-12B
safety certification on many different
processor architectures, with no
guarantee of being able to recoup
the non-recurring engineering (NRE)
costs.
For these reasons, DO-178B and ED-
12B Level A COTS RTOS certification
evidence packages have been
developed for the most widely-used
single-core processors in avionics.
Wind River has used a COTS evidence
approach for the VxWorks RTOS
which has enabled the significant
DO-178 and ED-12 certification NRE
costs to be amortised across multiple
customers and programmes using
the same processor architecture,
reducing the cost of certification on
each programme. This also results in
a virtuous circle, as these processors
have provided the lowest cost options
for follow-on certification projects,
due to the ability to reuse existing DO-
178 and ED-12 certification evidence,
rather than having to develop it for
a new processor architecture and
associated incremental costs.
The Challenge of Multi-
core Certification
50 l New-Tech Magazine Europe