functional safety management processes are relied upon to protect against errors being
introduced during perhaps 20 years of operation. Proof testing during operation should
reveal software errors that could be introduced, but as we will see later, most of the errors
found in code reviews would not be revealed by testing.
This paper discusses some of the counter measures that can be put in place to reduce the
likelihood of application software errors being introduced or remaining undetected, and
contrasts these measures with those required by IEC61511. In many cases, the software
anomalies found simply serve to highlight the benefits of applying Functional Safety
Management principles described in IEC61511 to all safety systems.
1.1
What is an FPSO?
A Floating Production Storage and Offloading vessel is usually a ship either purpose built or
converted from an oil tanker. FPSOs are typically around 300m long, and are moored in
offshore locations where they perform the same functions as offshore production platforms.
These include the separation and treatment of produced hydrocarbons and the injection of
treated seawater and gas into the reservoir. Unlike fixed platforms which generally pump
produced oil into a pipeline or to a remote loading terminal, the FPSO can store crude oil on
board, periodically offloading it directly to a shuttle tanker.
FPSOs are well suited to deep water applications, while their large storage capacity makes
them particularly effective as early production systems, where there is no oil pipeline.
Currently there are over 200 FPSOs operating worldwide.
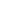
Figure 1: SBM Offshore’s FPSO Cidade de Paraty, sailing away from the shipyard
1.2
Terminology
On an FPSO there are typically three main safety instrumented systems. The following
terminology is used throughout this paper:
•
Process Shutdown System (PSS) – the hazard prevention system which detects
potentially dangerous conditions and executes process shutdowns, also known as
the Safety Instrumented System.