TAR NC Implementation Document – Second Edition September 2017 |
69
Multi-TSO Entry-Exit Systems
MULTI-TSO ARRANGEMENTS
Responsibility: subject to consultation per Article 26(1) by TSO/NRA, as NRA
decides; subject to decision by NRA
General
Article 10 addresses multi-TSO arrangements in entry-exit systems within one MS.
Current examples are Austria, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy and Spain. Article
11 addresses multi-TSO arrangements in an entry-exit system covering more than
one MS, like the current system that extends across Belgium and Luxembourg.
Application of same/different reference price methodology
jointly/separately by TSOs involved
Subject to exceptions, Article 6(3) of the TAR NC requires the application of the
same RPM to all entry and exit points in a given entry-exit system. This general rule
applies within a MS regardless of the presence of multiple TSOs in a given entry-exit
system.
The exceptions are in Article 10 for multi-TSO entry-exit systems within a MS, and
in Article 11 for multi-TSO entry-exit systems covering more than one MS. The
exception rules distinguish along two dimensions: (1) whether the RPMs are the
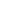
‘same’ or ‘different’ types; and (2) ‘joint’ and ‘separate’ RPM application. Figure 20
shows different options under Articles 10 and 11.
1)
1) ‘ITC’ stands for inter-TSO compensation.
ARTICLES
10 AND 11
Figure 20:
Multi-TSO arrangements in an entry-exit system within one MS and covering more than one MS
1)
multi-TSO e/e system
within 1 MS
joint
application
same
RPM
same
RPM
joint
application
same
RPM
different
RPMs
separate
application
same
RPM
different
RPMs
separate
application
ITC to
establish
no specific
conditions
\\
ITC to establish
\\
costs correspond to costs of
an efficient TSO
\\
max 5 years initially
\\
can be prolonged
default rule
not a default rule
exceptions
option in case
of a merger
not exceptions
covers >1MS