21
Ecosystem
degradation
Reusing processed
sewage
Contaminated
food provision
Drinking water treatment
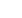
Global water withdrawal
percentage by sector
Waste water
discharge
Sewage sludge
Sewerage
Sewerage
Sewerage
Storm water
Storm water
Storm water
Agricultural run off
Agricultural run-off
Agricultural run off
Manufacturing waste
Manufacturing waste
Manufacturing waste
Industrial
Industrial
Industrial
Nuclear
Nuclear
Nuclear
Pharmaceutical
Microbes
Inorganic
particulate
material
Solid waste
Centralized and
decentralized sewage
treatment
Reed bed filtration
Enhancing nutrient
filtration of wetlands
Combined sewage
and storm water
Individual household
treatment
Municipality waste
management
Decreased
human health
Increased
production costs
Contaminated
food
Contaminated
drinking and
bathing water
Decreased ecosystem
health (e.g. dead zones)
Industrial small scale
waste management
Radioactive
Poisonous
Corrosive
Infectous
Suffocate/block
Smelly
Spills
Spills
Spills
Acquaculture
Acquaculture
Acquaculture
Medical
Medical
Medical
Organic matter
Chemicals
Biological
Heavy metals
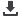
ORIGIN
IMPACT
TOXICITY
MANAGEMENT
Wastewater
Contaminants and their effects
Source: personal communication with E. Corcoran and E. Baker, UNEP-Grid Arendal.
Figure 5:
The contaminants in waste
water come from many different sources
and can have cumulative and synergistic
effects requiring a multi-pronged response.