Absolute
pressure (bar)
Boiling
temperature (°C)
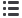
Heating
the refrigerant
initiates its evaporation
inside the evaporator
Blower
Evaporator
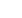
Condenser
Cooling fan
Cooling
the refrigerant
initiates its condensation
inside the condenser
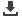
Absolute
pressure (bar)
Boiling
temperature (°C)
LOW PRESSURE SIDE
HIGH PRESSURE SIDE
2,34
-6,0°C
2,53
-4,0°C
2,72
-2,0°C
2,93
0,0°C
3,15
2,0°C
3,38
4,0°C
3,62
6,0°C
3,88
8,0°C
4,43
12,0°C
5,04
16,0°C
5,72
20,0°C
6,46
24,0°C
9,12
36,0°C
9,63
38,0°C
10,17
40,0°C
10,72
42,0°C
11,30
44,0°C
12,53
48,0°C
13,85
52,0°C
15,28
56,0°C
16,82
60,0°C
21,17
70,0°C
R134a
1. The fluid in the EVAPORATOR evaporates during
the thermal exchange with the hot air from the
exterior environment, thereby cooling down the
cabin.
10. The Air
conditioning
Loop
36
2. The fluid in the CONDENSER condenses during
the thermal exchange with the cooler air from the
exterior environment, thereby expelling the heat
to the exterior.
g
Two phase changes (evaporation / condensation)
g
Two phase changes at two different pressures
g
Two heat exchanges in two heat exchangers
(evaporator / condenser)
10.2.1 Boiling temperature vs pressure
The boiling point of the refrigerant governs heat
exchanges in the condenser and in the evapora-
tor: the refrigerant will evaporate or condense
depending on the heat exchange direction.