Training Aids & Simulators
L.
M.
J.
K.
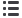
J. Injection Teaching Model
A26200..........................................................................
• Teaching model provides flesh-like surface for practice
of injection techniques. Biolike™ material can be
punctured repeatedly without showing holes. Injection
of liquid not recommended. Includes carrying case.
• Size: 6“x 4-3/4“x 1-3/4“ (15.6cm x 12.1cm x 4.4cm)
K. Hand Hygiene Chart
978-1-4511-9338-1 Laminated .....................................
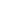
L. Male Model with Bladder
A26104..........................................................................
• This model allows students to practice locating the
urethra and inserting a catheter through it into the
bladder. Made of Biolike 2™, a soft fleshy feeling
plastic, this model features a visco-elastic urethra
that accurately duplicates the feeling of inserting a
lubricated catheter into the bladder. Carrying case
and lubricant included. Catheter not included. Size:
9” x 4” x 6” (22.9cm x 10.1cm x 15.2cm)
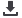
M. Female Model with Bladder
A26108..........................................................................
• Allows students to locate urethra and pass
lubricated catheter through it into bladder.
Made of Biolike™, a soft fleshy material, it has
a visco-elastic urethra. Lubricant included.
• Female 6“x 4“x 6“ (15.2cm x 10.1cm x 15.2cm)
Customers rate Anatomical Chart Company products
“Wonderful teaching tool”
Valerie, Dallas, TX
Hand Hygiene
Why is Hand Hygiene so Important?
Handsare themainpathways togerm transmissionduringhealthcare.
Therefore,goodhandhygiene is themost importantmethodofavoiding
spreadinggermsandpreventinghealth-careassociated infections.
When to Practice Hand Hygiene in Patient Care?
•Touchingapatient •Clean/asepticprocedure •GloveUse
Before
•Bodyfluidexposure •Touchingpatientorpatient surroundings •Gloveuse
After
PublishedbyAnatomicalChartCompany.Developed in consultationwithC.GlenMayhallM.D.
©2014
Wash handswhen visibly soiled.Otherwise, usehand rub.
Durationofhandwashingprocess:
40 –60 seconds.
Hand
Washing
Techniques
Hand
Rubbing
Techniques
Rub handswith alcohol forhand hygiene.Wash handswhen visibly soiled.
Durationof hand rubbingprocess:
20 – 30 seconds.
20-30
seconds
40-60
seconds
11
1
1
Oncedry,handsare safe.
10
Rinsehandswithwater.
Dryhands thoroughlywitha single-use towel.
Use towel to turnoff faucet.
8
8
Wethandswithwater.
Applyapalmfulofproduct inacuppedhand,coveringall surfaces.
Applyenough soap tocoverallhand surfaces.
2.Rubhands,palm topalm.
3.Leftpalmover rightdorsum (top
sideof righthand)with interlaced
fingers.Reverseandplace right
palmover leftdorsum (top sideof
lefthand)with interlacedfingers.
4.Placehandspalm topalm
withfingers interlaced.
5.Placebacksoffingers toopposing
palmswithfingers interlocked.
6.Clasp rightpalmaround left thumb
and rotate.Reverse -clasp leftpalm
around right thumband rotate.
7.Claspfingersof righthandand
rub leftpalm rotationallyback-
wardsand forwards.Reverse –
claspfingersof lefthandand rub
rightpalm rotationallybackwards
and forwards.
6
7
2
5
Oncedry,handsare safe.
9
3
4
Alcoholhand rubs arepreferredover handwashing because alcohol removesmicroorganisms from handsmorequickly and
effectively thanhandwashing.However, after caring for apatienton isolation forClostridiumdifficile infectionorNorovirus
infection,hands shouldbewashedwith soap andwater. Alcoholwill not kill these twomicroorganisms.
•Alcohol is lessdrying to the skin than handwashing.
•Hand careproducts shouldbeused regularly to keep skinof the hands ingood condition.
•Finger nail tips shouldbe kept short—not longer than¼ inch (.6 cm)
•Artificialnails shouldnotbewornby healthcareworkerswho care for high-riskpatients
Reminders
38
Nutrition Resources
39
Health Education
41
Training Aids
42
Anatomical
58
Skeletal
75
Gifts
76
Index
Resources
& Simulators
Models
Models