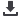
של המתג בצד הנמוך. דבר זה מראה לנו
קריטיות יכולות להיות
ac
שעקבות זרם
גם עקבות הארקה. זרמי חזרה כאלה
לא צריכים להיות מנותבים דרך משטח
הארקה. אם כן, הם יגרמו למשטח
ההארקה לראות היסטי מתח מבוססים על
ההשראות הטפילה של עקבת החזרה.
מראה כיצד יש לטפל בנתיב זרם
4
איור
. הוא חייב להיות מנותב
ac
ההארקה
בנתיב
vias
מקומית. אין להשתמש ב-
הארקה מקומי זה, מאחר שהם מוסיפים
השראות, מגדילים את היסטי המתח
וכתוצאה, יוצרים אף יותר רעש. בוודאות,
צריכה להיות
ac
עקבת חזרת זרם
בפוטנציאל הארקה, כך שאנחנו מחברים
עקבה זו אל משטח ההארקה בנקודה אחת
. דבר זה ישמור על זרמי
via
תוך שימוש ב-
כמקומיים.
ac
חזרת ה-
מנתיב חזרת זרם ההארקה
via
חיבור ה-
אל משטח ההארקה מסייע לנתק את מתח
ac
המשטח השקט מעקבת חזרת זרם ה-
המקומי הרועש.
של
ac
הפרת חוק זה ונטישת זרמי חזרה
ווסת מיתוג אל משטח הארקה יגרום
להקפצת כל משטח ההארקה ויגרום כל
מיני בעיות. משטחי ההארקה אמורים
לספק פוטנציאל ייחוס הארקה לתת-
מעגלים שונים במערכת ואמורים לסכך
. אם בצורה אידיאלית שום זרמים
RF
רעש
אינם מובלים על-ידי משטח ההארקה, הוא
יהיה שקט ובעל אותו מתח לכל אורכו.
רעש מעבר של מיתוג הוא לרוב בתחום
מגה-הרץ. הוא
300
מגה-הרץ עד
10
של
הרבה יותר גבוה בתדר מאשר תדר
המיתוג של ווסת מיתוג. לשם ניחות רעש
המשמש
LC
זה במוצא ספק-הכוח, מסנן
כרגיל להקטנת מתח גליות המוצא עשוי
לא להיות הבחירה הנכונה. חרוזי פריט
) הן הרבה יותר מתאימות לניחות
ferrite
(
תדרים גבוהים כאלה.
צלצול אחרי מעברי המיתוג
) מתח
ringing
ניתן לראות צלצול (
5
באיור
בצומת המתג אחרי מעבר מיתוג. יש לו
סיבות מרובות. העיקרית היא השפעות
טפילות והעובדה שזרימת הזרם לא ניתנת
לשינוי מיידי, אלא דורשת זמן מסוים כדי
לטפס דרך ההשראויות הטפילות.
snubbers
ניתן להקטין רעש זה על-ידי
) אקטיבי.
clamping
או מעגל ריתוק (
פאסיביים יפזרו את אנרגיית
Snubbers
הצלצול לתוך נגד וייצרו לבסוף חום.
מעגלי ריתוק אקטיביים מזינים חלקית
את האנרגיה של הצלצול לתוך המעגל, תוך
הגדלת היעילות הכוללת של ספק-הכוח.
פשוטים
dc
-
dc
לעתים קרובות, בממירי
אינם בשימוש,
snubbers
לא מבודדים,
מאחר שרוב הזמן, האנרגיה בצלצול
צומת-המיתוג איננה גבוהה מאוד, וגורמת
רק להפרעות קטנות. בספקי-כוח ממותגים
בצד הראשוני
snubbers
מבוססיי-שנאי,
או המשני או מעגלי ריתוק אקטיבי
דרושים לעתים קרובות יותר כדי להקטין
את הרעש.
צלצול במצב הולכת זרם
לא-רציפה
במצב של הולכת זרם לא רציפה
discontinuous
current
conduction
(
), ניתן לזהות צלצול מסוים
DCM
-
mode
בתדר נמוך בצומת המיתוג. אפשר לראות
לא-סינכרוניים בהם
buck
זאת בווסתי
Schottky
המתג בצד הנמוך ממומש בדיודת
). ווסתי
freewheeling
בבחירה חופשית (
סינכרוניים מציגים גם התנהגות זו
buck
במצב של חיסכון בהספק בעומס נמוך, כאשר
המתג בצד הנמוך איננו מופעל ומנותק בצורה
מובילה
MOSFET
אקטיבית ודיודת גוף ה-
את זרם הניתוק במקום זאת.
. הוא נגרם
6
הצלצול הסופי מתואר באיור
על-ידי העומס המתנדנד קדימה ואחורה
בצומת המיתוג בעל העכבה הגבוהה זמנית
כאשר זרם בסליל הוא אפס ושני המתגים
מכובים.
ככלל, כאשר מתכננים ווסת מיתוג עבור
הרעש הנמוך ביותר, אין לעצב את הווסת
. עבור אותו מתח מוצא,
DCM
כדי לפעול ב-
גורם לזרמי-שיא הרבה יותר
DCM
ה-
גבוהים בהשוואה למצב ההולכה בזרם
© 2015 How2Power. All rights reserved.
Page 3 of 8
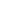
we indicate the current flow during the off-time. The schematic in the center shows this current path in green.
In the third schematic, we highlight all traces, where there is a difference in current flow between the top and
the center schematic. These are the traces in which we change current flow from full current to no current
within a few nanoseconds.
Fig. 3. Finding ac current traces in a switched-mode power supply.
«
«
בספק-כוח ממותג
ac
למצוא עקבות של זרם
.3
איור
מקומיות ואל תנתב אותן דרך משטח ההארקה
ac-
שמור על עקבות זרם ה
.4
איור
Exclusive Technology Feature
© 2015 How2Power. All rights reserved.
Page 4 of 8
These are the traces we need to keep as short as absolutely possible. This will reduce our parasitic inductance L
and thus reduce the generated voltage offsets after such switching transitions.
In the buck regulator example, this means that the input capacitor needs to be very close to the high-side
switch and also close to the ground connection of the low-side switch. This shows us, that critical ac current
traces can also be ground traces. Such return currents should never be routed through a ground plane. If they
are, they will cause the ground plane to see voltage offsets based on the parasitic inductance of the return
trace.
Fig. 4 shows how an ac ground current return path should be handled. It needs to be locally routed. Vias should
not be used in this local ground path, since they add inductance, increasing voltage offsets and as a result,
generate even more noise. Certainly, this local ac current ground return trace needs to be at ground potential,
so we attach this trace to the ground plane at one point using a via. This will keep the noisy ac return currents
local.
The via connection from the ground current return path to the ground plane helps to decouple the silent ground
plane voltage from the noisy local ac current return trace.
Fig. 4. Keep ac current traces local and do not route them through a ground plane.
Breaking this rule and dumping ac return currents of a switching regulator into a ground plane will make the
whole ground plane bounce and cause all kinds of trouble. Ground planes are supposed to give an accurate
ground reference potential to different subcircuits in the system and they are supposed to shield RF noise. If
ideally no currents are carried by the ground plane, it will be silent and have the same voltage all across it.
Switching transition noise is typically in the range of 10 MHz to 300 MHz. It is much higher in frequency than
the switching frequency of a switching regulator. For attenuation of this noise on the output of the power
supply, an LC filter, commonly used to reduce the output ripple voltage, may not be the right choice. Ferrite
beads are much bett r suited to attenuate such high frequencies.
Ringing After Switching Transitions
Voltage ringing on the switch node after a switching transition can be seen in Fig. 5. It has multiple causes. The
main one is mostly parasitic influences and the fact that current flow cannot change instantaneously, but
requires some time to ramp up through parasitic inductances.
Such noise can be reduced by snubbers or active clamp circuitry. Passive snubbers will dissipate the energy of
this ringing into a resistor ultimately generating heat. Active clamp circuitry is feeding the energy of the ringing
partially back into the circuit, increasing the overall efficiency of the power supply.
Often, in simple nonisolated dc-dc converters, snubbers are not used, since most of the time, the energy in the
switch-node ringing is not very high, causing only small disturbances. In transformer-based switched-mode
SMART HOME
מוסף מיוחד
New-Tech Magazine l 70