25
2
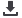
used in various ways, such as handheld, attached to the jacket of a speaker or it can be placed on a table
(Figure 3A). The system may be of use in steady-state situations such as meetings, dining and at home in
family situations. Especially when the microphone is placed near the speaker, a significant improvement
of the signal to noise ratio can be obtained. The listener with impaired hearing must change the direction
of the microphone manually if the source of interest moves around. The microphone can be used in an
omni-directional, zoom and super-zoom mode. Based on the technical specifications, an articulation index
weighted directivity index of the system, was calculated of approximately 8 dB for the microphone in
super-zoom mode. Figure 3B shows the articulation index weighted polar diagram with an opening angle
of approximately 130° (-6 dB point) and average noise reduction from the behind of 13 dB. During the
experiment, the Handymic was placed on a one meter high stand, in front of the speech loudspeaker at 75
cm distance and in super-zoom mode. This simulated a listener holding the Handymic in his hand just in
front of the body. We measured the sound level at 75 cm, with speech noise coming from the loudspeaker.
Compared to a distance of 100 cm (center of the sphere), an increase was measured of the front signal
of +1.5 dB. This will result in a difference in the speech-tonoise ratio of +1.5 dB compared to the center
position. The Handymic’s signal was sent to the speech processor by the wireless Microlink FM-system with
the FM receiver by Bruckhoff Apparatebau (Hannover, Germany, type MicroLink CI+).
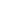
The Linkit array microphone system was developed as an assistive listening device for people with hearing
impairment, with hearing aids either behind the ear or in the ear (Figure 3C). Its use is mainly intended
for situations with background noise such as at parties and restaurants. While wearing the Linkit on the
head, the user can move freely and pick out the signal in front. A hearing aid user can use the Linkit
over the ear. The microphone’s signal can be transmitted to the hearing aid wirelessly via induction. The
array processing is based on the fixed sum beam forming, with three microphones inside the bar (Soede,
Berkhout, & Bilsen, 1993a, Luts et al. 2004). The articulation index weighted directivity index equals 7 dB
(measured on the head of KEMAR, Knowles, Itasca, IL). Figure 3D) gives the articulation index weighted
polar diagram. Compared to the Handymic, the opening angle of 100° is slightly narrower while the average
noise reduction from behind is 10 dB. The Linkit has an external audio output for use with the standardized
Direct Audio Input (DAI) connector behind the hearing aids. This output signal of the Linkit was not yet
fully adapted for use with the Clarion CII. A wire measuring 90 cm in length was used to connect the
Linkit to the audio input of the speech processor for use with cochlear implants. To match the input-output
sensitivity of the Linkit and the input of the processor of the cochlear implant, a 20 dB buffer-amplifier was
used. During the tests, the Linkit was placed on the ear, contralaterally to the headpiece.
The output spectra of the Handymic and the Linkit were compared with each other. They were equal to
each other within a margin of ±3 dB, within the frequency range of 500 and 4000 Hz.
Subjects and Test Sequence
25 Cochlear implantees who had been implanted at Leiden University Medical Centre and had more
than 3 mo of experience with the implants, were invited to come to the hospital for an evaluation of the