28 | Chapter 2
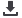
subject were fitted with a psychometric curve. The group scores at SNR with fewer data points could be
calculated using these psychometric curves. For the fitting, a x 2
function with three degrees of freedom was
used as described by Schön et al. (2002). This function is equal to:
u
(
x
) =
u q
x
x 2
[ 2.37 +
k
× (
x - x
0.5)]
where
u
is the speech reception score (in %) and
u
q the fitted score in quiet surroundings. The constant
k
is
proportional to the gradient of the curve at 0.5 X
u
q ,
x
is the signal-to-noise ratio, and
x
0.5 is the signal-to-
noise ratio at 0.5 X
u
q . The parameters
u
q ,
k
and
x
0.5 were used to fit the curve to the data.
RESULTS
Figure 4 shows the individual results (phoneme scores) for the CVC tests as obtained for all subjects
with normal hearing and the cochlear implant users with the three different microphones. All cochlear
TABLE 1. Demographics of cochlear implant users involved in this study
Results of standard clinical tests
Subject
Age at
implantation
Duration of
severe deafness
(yr)
CI-use
(mo at moment of study)
Etiology
Phoneme score in
quiet (65 dB SPL)
Duration of CI-use
for clinical test data
in quiet surroundings
A
23
0.5
4
Meningitis
93
3 mo
B
62
4
21
Progressive
84
1 yr
C
38
37
20
Hereditary progressive
67
1 yr
D
39
36
19
Aminoglycosides
98
1 yr
E
49
2
9
Left unknown,
Right glomustumor
71
6 mo
F
14
0.2
12
Meningitis
87
1 yr
G
43
39
13
Hereditary
89
1 yr
H
59
1
10
Sudden deafness
96
1 yr
I
52
23
14
Unknown
83
1 yr
J
59
1
18
Menie`re’s disease
88
1 yr
K
50
20
3
Unknown
82
3 mo
L
67
20
5
Noise induced
96
3 mo
M
49
15
12
Progressive
98
1 yr
The table gives the age at implantation, durations of severe deafness, CI-use and etiology. The last two columns give the average phoneme score in quiet surroundings obtained prior to the
study, and the experience with the CI device at the time of the clinical test. All subjects were implanted with one cochlear implant. No hearing aid device was used in the contralateral ear.
TABLE 2. Clinical results of 13 cochlear implant users, using their standard program
Phoneme scores at SNR (%) in a standard set-up with speech and noise from one loudspeaker
Headpiece Quiet
10 dB
5 dB
0 dB
5 dB
10 dB
15 dB
Word scores (%)
0 dB
Average
88
74
64
47
36
[8]
—
—
26
SD
9
17
14
18
8
—
—
14
The mean phoneme scores on the CVC word test in a standard set-up with speech and noise from the same loudspeaker (speech at a fixed level of 65 dB SPL, free field, 11 words per data
point) in quiet surroundings and in background noise with SNRs of 10, 5, 0, 5, 10 and 15 dB. The mean values are given per SNR for the results of the standard listening tests done
prior to this experiment. The numbers between the brackets denote the number of cochlear implant users tested at 5 dB. The last column gives the word-score at SNR 0 dB as a
comparison.
TABLE 1. Demographics of cochlear implant users involved in this study
Results of standard clinical tests
Subject
Age at
implantation
Duration of
severe deafness
(yr)
CI-use
(mo at moment of study)
Etiology
Phoneme score in
quiet (65 dB SPL)
Duration of CI-use
for clinical test data
in quiet surroundings
A
23
0.5
4
Meningitis
93
3 o
B
62
4
21
Progressive
84
1 yr
C
38
37
20
Hereditary progressive
6
1 yr
D
39
6
9
Aminoglycosides
98
1 yr
E
4
2
9
Left unknown,
Right glomustumor
71
6 mo
F
14
0.2
2
ingitis
7
1 yr
G
43
39
1
Hereditary
9
1 yr
H
59
1
10
Sudden eafness
1 yr
I
52
23
4
Unknown
83
1 yr
J
59
1
18
Menie`re’s disease
88
1 yr
K
50
20
3
Unknown
82
3 mo
L
67
20
5
Noise induced
96
3 mo
M
49
15
12
Progressive
98
1 yr
The table gives the age at implantation, durations of severe deafness, CI-use and etiology. The last two columns give the average phoneme score in quiet surroundings obtained prior to the
study, and the experience with the CI device at the time of the clinical test. All subjects were implanted with one cochlear implant. No hearing aid device was used in the contralateral ear.
TABLE 2. Clinical results of 13 cochlear implant users, using their standard program
Phoneme scores at SNR (%) in a standard set-up with speech and noise from one loudspeaker
H adpiece Quiet
10 dB
5 dB
0 dB
5 dB
10 dB
15 dB
Word scores (%)
0 dB
Average
88
74
64
47
36
[8]
—
—
26
SD
9
17
14
18
8
—
—
14
The mean phoneme scores on the CVC word test in a standard set-up with speech and noise from the same loudspeaker (speech at a fixed level of 65 dB SPL, free field, 11 words per data
point) in quiet surroundings and in background noise with SNRs of 10, 5, 0, 5, 10 and 15 dB. The mean values are given per SNR for the results of the standard listening tests done
prior to this experiment. The numbers between the brackets denote the number of cochlear implant users tested at 5 dB. The last column gives the word-score at SNR 0 dB as a
comparison.
The table gives the age at implantation, durations of severe deafness, CI-use and etiology. The last two columns give the average
phoneme score in quiet surroundings obtained prior to the study, and the experience with the CI device at the time of the clinical
test. All subjects were implanted with one cochlear implant. No hearin aid device was used in the contralateral ear.
The mean phoneme scores on the CVC word test in a standard set-up with speech and noise from the same loudspeaker (speech
at a fixed level of 65 dB SPL, free field, 11 words per data point) in quiet surroundings and in background noise with NRs of 10, 5,
0, 5, 10 and 15 dB. The mean values are given per SNR for the results of the standard listening tests done prior to this experiment.
The numbers between the brackets denote the number of cochlear implant users tested at 5 dB. The last column gives the word-
score at SNR <?> 0dBasa comparison.