A GLOBAL OUTLOOK ON METHANE GAS HYDRATES
31
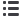
Undeformed muds
Seafloor mounds
Fractured muds
Marine sands
Arctic sands
Gas Hydrate In-place Resources:
Favorability for production correlates
closely with the nature of the host sediment
3 Tcms
300 Tcms
3 000 Tcms
??? Tcm
??? Tcm
1990
2030
30 Tcms
“Conventionals”
Early Unconventionals (tight gas; shallow shales)
Emerging Unconventionals (CBM, deep shales)
Methane Hydrates
Geopressured Brines
and others
30 Tcms
300 Tcms
3 000 Tcms
3 000 Tcms
1950
1860
Approximate date of first
significant commerciality
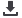
Increasing in-place resource volumes
Decreasing resource quality and concentration
Decreasing resource recoverability; increased
Dependance on technology
Increasing in-place resource volumes
Decreasing resource quality and concentration
Decreasing resource recoverability
Increasing dependance on technology
Approximate Recoverable Resources
In-place Volumes:
Recoverability To Be Determined
In-place Volumes:
Recoverability
To Be Determined
Resource pyramid for gas hydrates
Source: redrawn from Boswell and Collett, 2006
f r
r
r t r m
ri
r ti
r t I - l
r :
r ilit f r r
ti rr l t
l
l it t t r f t
t
i
t
3 000 Tcms
cm
“
ti
l ”
rl
ti
l (ti t
;
ll
l )
r i
ti
l (
,
l )
Metha
r t
r
r ri
and others
1950
r i
t t f r t
i i
t
r i lit
I r i i - l
r
r l
r i r
r
lit
tr ti
r i r
r r
r ilit ; i r
t
l
I r i i - l
r
r l
r i r
r
lit
tr ti
r i r
r r
r ilit
I r i
t
l
r i
t
r l
r
I - l
l
:
r ilit
t r i
I - l
l m :
r ilit
t r i
S rce: re ra fr
s ell a
llett, 2006