31
Chemical Technology • January 2015
Minerals Processing
and Metallurgy
bcc-based B2 (Pearson symbol
c
P2) or CsCl-structure for
composition AB, and fcc-based C1 (Pearson symbol
c
F12)
or CaF
2
-structure for composition AB
2
. This again confirms
the three requirements stipulated above that coloured in-
termetallic compounds need to have a crystal structure of
highest symmetry ensuring a sufficiently simple electronic
structure for distinct absorption bands of high intensity.
According to this approach, only the following potential
coloured binary gold, palladium and platinum intermetallic
compounds can result:
CsCl-structure: PdIn, PdBe, PdMg
CaF
2
-structure: PdAl
2
, PtSn
2
, PtGa
2
, PtAl
2
, PtIn
2,
AuGa
2
,
AuAl
2
, AuIn
2
.
Element B is of Groups 13 and 14 in the Periodic
Table with the exception of PdMg. Further, PtAl (tetragonal
structure) also exhibits colour according to Figure 1 [33].
Hume-Rothery electron concentration
An electron-to-atom ratio is stipulated for the Hume-
Rothery phases, where the electron concentration (e/a)
is defined as the sum of the valence electrons per atom of
the compound:
e/a
= 1/100 -
Σ
a
i
v
i
where a
i
is the concentration in at.%, and
v
i
is the number of valence electrons of the element
i
.
(a)
(b)
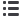
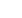
Figure 1: Regions of high-symmetry structure in the AB (a) and AB
2
(b) Pettifor maps.
Mendeleev numbers and prototypes (c is cubic, t is tetragonal, o is orthorhombic, h
is hexagonal) are shown. Limits for expected coloured intermetallic compounds are
shown by the dashed line [33].
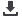
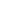
Figure 2: Crystal structures: (a) CsCl-structure, and (b) CaF
2
-structure.
(a)
(b)
Purple Gold
TM
Patent Number 82596 Aspial Corporation
www.purplegold.com. Jewellery available from Lee Hwa Jewellery and Goldheart, both in Singapore