ENERGY + ENVIROFICIENCY
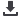
Figure 4: Dijkstra’s Algorithm run for case 1, Path from CB2 to DG4.
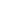
Figure 5: Dijkstra’s Algorithm run after new deployments, Path from
CB2 to DG6.
Conclusion
OO based models are proposed for microgrid modelling. The pro-
posed models make it possible to define information data specific
to various electrical nodes within a network in terms of connections
between the nodes and the devices connected to these nodes. In this
manner the changing structure of a particular network can be fol-
lowed and the new operating points can be calculated, then updated.
After modelling the microgrid according to graph theory, Dijkstra’s
algorithm is implemented to find the path from the point of common
coupling to different parts of the network. This algorithm extracts the
hierarchy of different components in the network. This feature is very
crucial for plug and play purposes in electrical networks.
Acknowledgement
The author presented this topic at the ICUE conference in Cape Town
in 2014.
References
[1] Ustun TS et al. 2011. Recent developments inmicrogrids and exam-
ple cases around the world - A review. Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews.
[2] Lasseter B. Microgrids. IEEE 2001 WM Panel: Role of Distributed
Generation in reinforcing the Critical Electric Power Infrastructure.
take note
Taha Selim Ustun received a BE degree in Electrical and Electron-
ics Engineering from Middle East Technical University, Turkey
in 2007 and a Master of Engineering Science degree from the
University of Malaya, Malaysia in 2009. He has a PhD in Electri-
cal Engineering from Victoria University, Melbourne, Australia.
Currently, he is an Assistant Professor in Electrical Engineering,
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnagie-Mellon University, PA,
USA. His research interests are Power Systems Protection, Communication in
Power Networks, Distributed Generation, Microgrids and Smartgrids. Enquiries:
• The lessons learned in distributed control systems are
now being applied in power network control.
• New algorithms of control are continually evolving as
we require more and more ‘intelligence’ in our power
networks.
• Dijkstra’s algorithm has been shown to be applicable to
determining the path from point of common coupling to
different parts of the network – enhancing our ability to
understand the network operation.
[3] UstunTS,etal.Investigationofmicrogridbehaviourwhileoperatingunder
variousnetworkconditions.PresentedattheIEEEInternationalConference
on Smart Grid Engineering (SGE 12), UOIT, Oshawa, Canada, 2012.
[4] El-Tamaly HH and El-sayed AHM. A new technique for setting
calculation of digital distance relays. Power Systems Conference,
2006. MEPCON 2006.
[5] OsmanAH,etal.2005.Transmissionlinedistancerelayingusingon-line
trainedneural networks. PowerDelivery, IEEETransactions, Volume20.
[6] OudalovAandFidigatti A. Adaptivenetwork protection inmicrogrids.
More Microgrids Europe.
www.microgrids.eu/documents/519.pdf.[7] Ustun TS, et al. 2011. A microgrid protection system with central
protection unit and extensive communication. Environment and
Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), 2011 10th International Conference.
[8] Ustun TS, et al. 2012. Fault current coefficient and time delay as-
signment for microgrid protection systemwith central protection
unit. Power Systems, IEEE Transactions, Volume PP.
[9] Ustun TS, et al. 2011. A central microgrid protection system for
networks with fault current limiters. Environment and Electrical
Engineering (EEEIC), 10th International Conference 2011.
[10]Ozansoy CR, et al. 2009.Object modelling of data and data sets
in IEC 61850. Power Delivery, IEEE Transactions, Volume 24.
[11]Ozansoy CR, et al. 2009. The application-viewmodel of IEC 61850.
Power Delivery, IEEE Transactions, Volume 24.
[12]WG17> Introduction to IEC 61850-7-420: Distributed Energy Re-
sources (DER) Object Modelling. White Paper, Volume. Ver2. 2009.
[13]Ustun TS, et al. 2011. Implementation of Dijkstra’s Algorithm
in a Dynamic Microgrid for Relay Hierarchy Detection. Second
IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications
(SmartGridComm), Belgium.
[14]Faria P. 2009. Shortest path with Dijkstra and C#. Available: http://
letmetutoryou.wordpress.com/2009/05/26/shortest-path-with-dijkstra-and-c/
39
September ‘15
Electricity+Control