* Visit
inorganicventures.com/tech/icp-operations/for additional information from this link
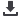
Water at pH of 7
Dilutions in water at pH 7 are not as common for
most elements but may be required to prevent
chemical reactions of some of the compounds
containing the element. Please note that solutions
at pH 7 may support biological growth and
therefore the long-term stability should be
questioned.
Those elements that may have an advantage to
being diluted in water at pH 7 are shaded in
yellow to the right:
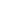
Hydrofluoric Acid Matrices
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) requires the use of HF-
resistant introduction systems. These systems are
more expensive than glass, have longer washout
times, and give a larger measurement precision.
However, there are times when the use of HF
offers a major advantage over other reagents.
Those elements where an HF matrix may be
optimal are shaded in green below:
1. HF is used for Si
3
N
4
preparations and other
nitrides.
Sulfuric Acid Matrices
Sulfuric acid (H
2
SO
4
) is commonly used in preparations and therefore added to standards in combination with other acids.
Elements that either benefit or comfortably tolerate the presence of H
2
SO
4
are shaded in orange below:
1. Dilutions of Hg and Au in H
2
SO
4
below 100
ppm should be stored in borosilicate glass due to
adsorption on plastic.
2. Trace levels of HCl or Cl
-
will form AgCl,
which will photoreduce to Ag
0
.
F
denotes that the element can be diluted in
H
2
SO
4
if complexed with F
-
.
Cl
denotes that the element can be diluted in
H
2
SO
4
if complexed with Cl
-
.
HF
denotes that the element should have excess
HF present when diluted with H
2
SO
4
.
T
denotes that the tartaric acid complex can be
diluted in H
2
SO
4
.
Phosphoric Acid Matrices
Phosphoric acid (H
3
PO
4
) is not commonly used in preparations since it attacks glass, quartz, porcelain, and Pt containers at
elevated temperatures (greater than 100 °C). However, the presence of
3
PO
4
will not adversely effect any of the elements at low
μg/mL levels and below.