21
Figure 1.7
rainfall evaporates as soon as it falls, 20 per cent
is lost through evapotranspiration and an
average of 14 per cent is available as surface
runoff (Chenje 2000).
Average annual rainfall across the river basin
varies from 500 mm in the extreme south and
southwest part of the basin to more than
1 400 mm in the Upper Zambezi and Kabompo
sub-basins, in the north-eastern shores of Lake
Malawi/Nyasa/Niassa in Tanzania, and in the
southern border area between Malawi and
Mozambique (Chenje 2000).
Rainfall is greatest in the north, with an
extensive area receiving over 1 000 mm, and
declines towards the south, where most areas
receive less than 700 mm (SADC and ZRA
2007). In general, there is only a single rainy
season in the year. Rainy seasons are longer in
the north and northeast, and much shorter in
the southwest.
NAMIBIA
ANGOLA
BOTSWANA
ZAMBIA
ZIMBABWE
MOZAMBIQUE
TANZANIA
MALAWI
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC
OF CONGO
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
C
u
a
n
d
o
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
K
a
b
o
m
p
o
L
u
a
n
g
w
a
M
a
z
o
e
S
h
i
r
e
S
h
a
n
g
a
n
i
K
a
f
u
e
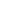
December
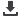
12 14 16 18 20 22 24 °C
NAMIBIA
ANGOLA
BOTSWANA
ZAMBIA
ZIMBABWE
MOZAMBIQUE
TANZANIA
MALAWI
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC
OF CONGO
L
u
n
g
w
e
b
u
n
g
u
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
C
u
a
n
d
o
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
K
a
b
o
m
p
o
L
u
a
n
g
w
a
M
a
z
o
e
S
h
i
r
e
S
h
a
n
g
a
n
i
K
a
f
u
e
L
u
n
g
u
e
B
u
n
g
o
Zambezi River Basin average temperature
July
Sources: Denconsult 1998. ZACPLAN Sector Studies:
Introductory Volume. Final Report. Southern African
Development Community and Zambezi River Authority,
Lusaka; Chenje, M. (Ed.) 2000. State of the Environment
Zambezi Basin 2000. SADC/IUCN/ZRA/SARDC,
Maseru/Lusaka/Harare