21
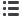
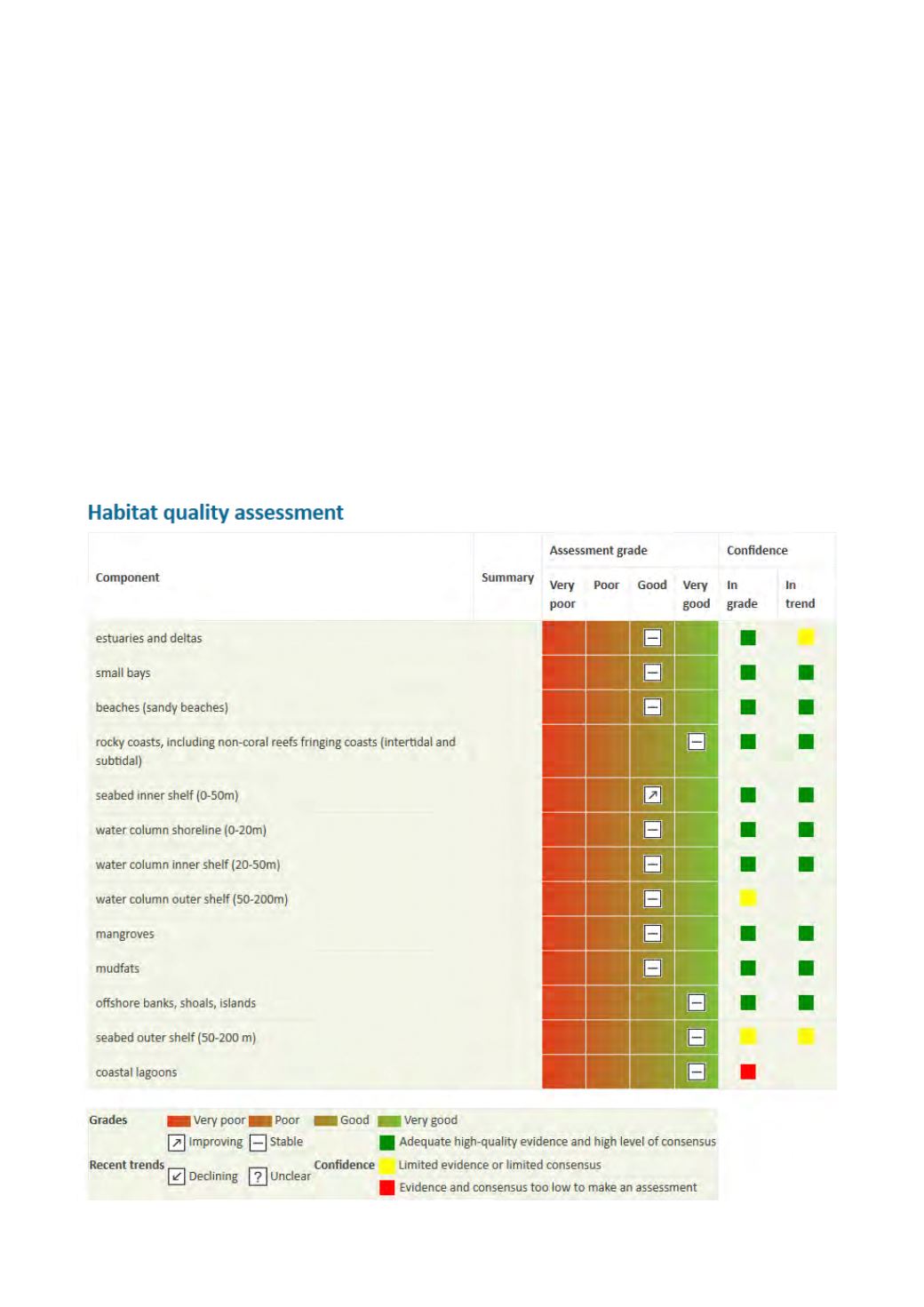
Figure 4.1:
Summary of the habitat assessment for “most” places
Oceanic habitats reach from the shoreline to the deep sea.
Surface marine waters in the tropics are generally depleted
in nutrients but in certain coastal regions, the nutrients are
locally enhanced as a result of upwelling. The Sierra Leone
coast as part of the Guinea Current coast is characterized
by such an upwelling which is seasonal and occurs from
Cape Palmas to Benin Republic.
The shallow coastal waters of the Sierra Leone have a
highly diverse fish and invertebrate fauna, many of which
are important in commercial fishing. Fish diversity in
the coastal waters is reasonably well documented (FAO
1990). What is poorly known is the diversity of the benthic
macro-fauna i.e. animals that live on the bottom or within
the bottom sediment and can be retained on a 0.5 mm
4. Habitat
sieve. The situation is much worse for the meiofauna i.e.
organisms smaller than 0.5 mm. Sub-tidal benthic habitats
are among the least studied in the waters of the Sierra
Leone Continental shelf.
According to the assessment resulting from the workshop
held in Freetown in February 2014, thirteen (13) habitats
were assessed (Fig. 4.1).
4.1. Estuaries and deltas
While Sierra Leone is developing its fishing, mining
and tourism industries, it is faced at the same time with
intense rate of urbanization of the coastal areas. Owing
to the increase in coastal population, coupled with