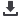
input is grounded. Note for IB+, a
negative value means the current
flow out of the +IN terminal. For
IOUT, a negative value means the
current flow out of the –IN terminal.
Taking ADA4077-2 with V+ absent
as an example, V+ is clamped to the
VIN voltage by an ESD diode.
VIN is connected to V+ via an ESD
clamp diode, so when VIN is 0 V, V+
is –0.846 V.
Current flow path loop: as the red
path shown in Figure 4, 0.7 mA
current flows from GND (+IN) to
V+. 1.6 mA current flows from GND
(+IN) through an internal resistor,
D5 and the feedback path between
–IN and OUT, then the current flow
into output terminal. Finally the
two currents (0.7 mA and 1.6 mA)
combine to flow to –15 V, and the
combined current flows back to GND
(+IN).
Results are similar between the
ADA4177-2 and ADA4077-2. Note
that within the ADA4177-2, D1 is
implemented by an emitter base of a
lateral PNP transistor. The transistor
routes the overvoltage current away
from the V+ to the V–. The ADA4177
circuit in Figure 4 shows 9.1 mA
current flow from V+ back to V– ,
and combined with 0.2 mA current
in the feedback path, results in a 9.3
mA current flow to –15 V, then the
current flows back to GND.
No large currents are observed
at the input pins and power pins
for either the ADA4077-2 or the
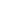
Figure 2. ADA4077/ADA4177 simplified block diagram
Table 3. Internal Diode of an Op Amp
Table 4. ADA4077-2/ADA4177-2 Results with Floating Input
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 29