The Normal 12-Lead EKG
59
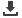
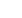
The duration of the QT interval is proportionate to the heart rate.
The faster the heart beats, the faster it must repolarize to prepare for
the next contraction; thus, the shorter the QT interval. Conversely,
when the heart is beating slowly, there is little urgency to repolarize,
and the QT interval is long. In general, the QT interval constitutes
about 40% of the normal cardiac cycle, as measured from one R wave
to the next.
A
B
QT Interval
R-R Interval (1 cycle)
QT Interval
R-R Interval
The QT interval constitutes about 40% of each cardiac cycle (R–R
interval). The faster the heart beats, the shorter the QT interval. The
heart rate in
B
is considerably faster than that in
A
, and the QT interval
is correspondingly much shorter (less than one and one-half boxes vs.
two full boxes).