to climate change, biodiversity, water and soil as well as labour conditions,
indigenous people’s rights, land rights and food security. The “UN energy
report” warns: “Unless new policies are enacted to protect threatened lands,
secure socially acceptable land use, and steer bioenergy development in a
sustainable direction overall, the environmental and social damage could in
some cases outweigh the benefits”. Governments as well as the private sector
need to take coordinated action to ensure sustainable production and use of
biofuels, so that they may play a useful role in the transformation of the en-
ergy sector. Internationally agreed sustainability principles and criteria; iden-
tification, designation and monitoring of “no go areas” with regard to carbon
storage and biodiversity potentials; social safeguards that ensure that vulner-
able people are not disadvantaged through food and energy price increases,
and access to modern forms of energy are among the elements taken into
account by UNEP as they are collaborating with others on the development of
criteria to maximize development benefits of bioenergy.
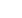
Source: Emmanuelle Bournay,
Atlas Environnement du Monde Diplomatique 2007.
* Under the high productivity farming conditions that are prevailing today.
In red: main concerns related to biofuels
Agricultural
prices up
Deforestation
Land use change
Monoculture
Land use competition
with food production
Massive need for agricultural land
In green: virtuous initial
equation in favour of biofuels
Crops are
renewables
No
Greenhouse
gas emission
Petrol and
diesel
substitution
Biofuels
Final use
(road transport)
Agricultural production*
Global process:
Production and use of fertilizers
Use of farm machinery
Industrial transformation process
Distribution
In blue: main concerns
related to fossil fuels
Fossil fuel
shortage
Fossil fuels
Limited
resource
Global process:
Biodiversity
damage
Prospecting
and extracting
Transport
Refining
Distribution
Final use
(road transport)
Fossil fuel
burning
(petrol and
diesel use)
Greenhouse gas
emission
CLIMATE
CHANGE
FAMINE, MALNUTRITION
and other HEALTH CONCERNS
Water
and soil
pollution
Biofuel versus fossil fuel
Threats