Principle
Advantages
Drawbacks
Site
constraints
Principle
Advantages
Drawbacks
Site
constraints
Currently attractive for investors
*
High production rate (efficiency)
*
Mature technology
High production rate (efficiency)
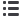
Wind
*
Landscape artificialization
(visible areas)
*
Danger for birds and bats
*
Noise
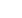
Hydroelectricity
Source: UNEP-GRID-Arendal,
Vital Climate Graphics
, 2005; Godfrey Boyle,
Renewable Energy: Power for a Sustainable Future
, 2004.
Availability of water resource is critical
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
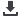
Geothermal
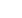
Ocean
Energy captured from wind by turbine
blades is transmitted to a generator
to produce electricity.
Energy captured from falling freshwater
by turbines is transmitted to a
generator to produce electricity.
Water basin disruption:
*
Big dams flood regions (community
and economy lose usage)
*
Artificialized riverbanks and dams
harm fauna and flora.
Needs strong wind
(high points and plateaux)
Energy bill reduction
*
Needs outside surface (garden)
*
High cost for installation
*
Needs electricity to run the heat
pump (unless wood is used)
*
Landscape artificialization
*
Community and economy lose
usage (tourism)
*
Artificialized coastlines harm fauna
and flora.
The power of the tidal flows or waves
runs turbines.
Naturally stable groundwater warms
up or cools a water circulation system
(local scale) or the steam runs a
turbine (power plant).
Greatest efficiency in volcanic regions
Needs accessible coastline
and high tidal fluctuation