Introducing
the main
renewable
energies
* If you except indirect emissions from building the plants, dams, turbines, solar panels, etc.
Minimal maintenance
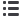
Solar (photovoltaic)
GHG emissions from
land use change
GHG emissions from
land use change
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
n o G H G e m i s s i o n s *
Biomass
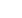
Solar thermal
Wood
Waste
Biofuels
(ethanol and biodiesel)
A semiconductor cell (usually
made from silicon) converts
sunlight directly into electricity.
A surface absorbs and
transfers heat and light rad-
iated from the sun to a fluid.
Minimal maintenance
Currently attractive for investors Energy bill reduction
*
Needs large panel surface
*
Used cells are hazardous
waste
*
Visual impact
*
Needs large panel surface
*
Used cells are hazardous
waste
*
Visual impact
Depends on length of daily
sunlight and intensity
Depends on length of daily
sunlight and intensity
Problematic at industrial
scale (planting fast-growing
trees, monoculture)
Problematic at industrial
scale:
*
Surface competition with
food crops, monoculture
*
Deforestation, fertilizers
Replace fossil fuel burning
from transport
*
Uses waste as a resource
*
Reduces methane emissions
Feedstock can be wastewood
Distance to wood production
areas is critical
Availability of agricultural
lands is critical
Distance to landfill / manure
production areas is critical
Either alcohol (from sugar,
starch or cellulose crops
fermentation) or oil is used
to fuel engines.
Methane from waste
decomposition is harnessed
to produce heat or run
a turbine.
Biogas needs to be “cleaned”
of corrosive hydrogen sulfide
The steam from wood burning
runs a turbine or is used
directly for the building.
Transport
Electricity production
Applications:
Industrial process
Heating or cooling
buildings
Warming water
On-site use mostly