(SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC), the nonparametric Wilcoxon
ranked sum test was employed to assess significance of findings
for all analyses between CRS subclasses. Spearman coefficient
of rank correlation test was utilized to calculate correlations
between the measurement tools for each subclass of CRS and
control group.
Histopathology and Immunostaining
Informed consent was obtained prior to obtaining the
nasal polyps in patients who failed medical treatment for CRS
and were undergoing ESS. The nasal polyps specimens for the
study groups were taken specifically from the ethmoid sinuses
or polyps in the ostiomeatal complex. For the control group, eth-
moid sinus mucosa was taken during the CSF leak repair. All of
the patients did not receive oral steroid 4 weeks prior to the
specimen collection. Tissue samples were then evaluated for eo-
sinophils (EO),
polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN),
lymphocytes, and plasma cells with hematoxylin and eosin
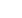
(H&E) staining. Degree of fibrosis was measured using Masson
trichrome staining (Fig. 2). Mast cells were identified with
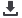
CD117 immunostaining (Fig. 3).
For the H&E staining, nasal polyps were evaluated for the
area with the most dense cell populations similar to standard
clinical evaluation of any pathologic tissue. This location of the
dense collection of inflammatory cells was determined as either
Fig. 2. Degree of fibrosis was graded on level of trichrome stain-
ing. (A, B, C) Representative scores 0, 1, and 2, respectively.
Fig. 3. Mast cells stained with CD117.
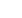
Fig. 4. Microscopic hematoxylin and eosin slide (2
3
) of a nasal
polyp demonstrating stromal distribution of cells within the circle.
Laryngoscope 123: March 2013
Han:
Subclassification
of Chronic
Sinusitis
49