57
New Biological Frontiers Illuminated by Molecular Sensors and Actuators
Poster Abstracts
23-POS
Board 23
Some Like It Hot: Biomolecule Analytics Using MicroScale Thermophoresis
Zhuo Li
, Moran Jerabek-Willemsen, Philipp Baaske, Stefan Duhr.
NanoTemper Technologies, Munich, Germany.
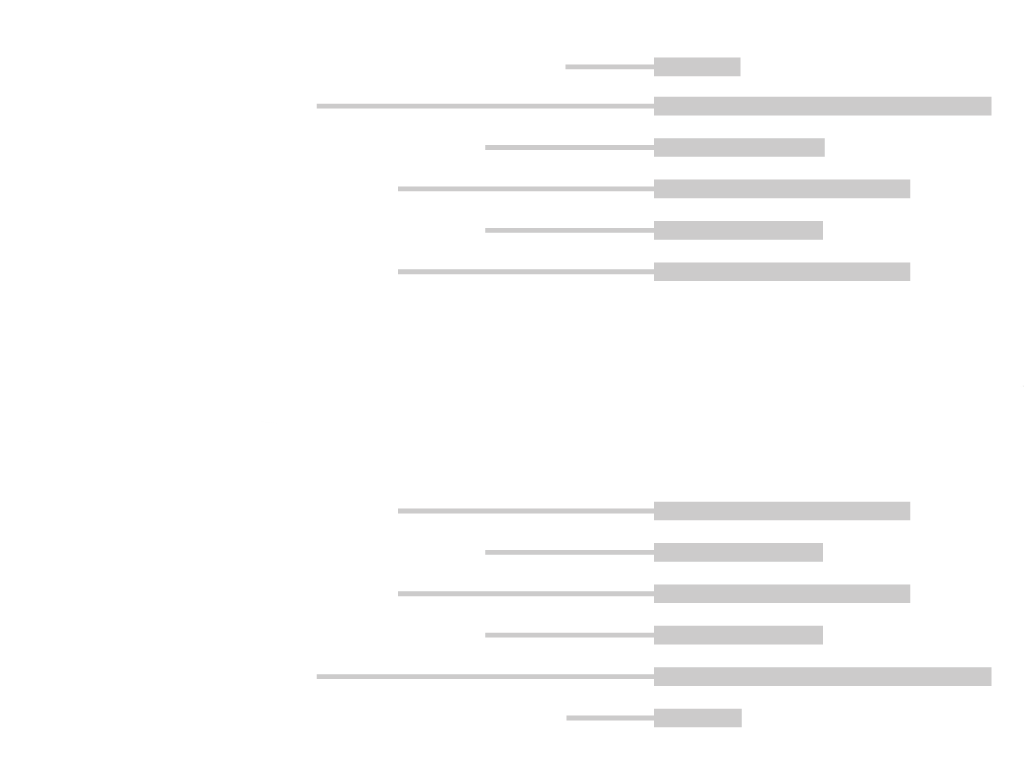
The analysis of biomolecular interactions and their quantification in the early stages of the drug
discovery allows faster development of therapeutics and diagnostic techniques. MicroScale
Thermophoresis (MST) is a novel and exciting technology to quantify biomolecular interactions
and to enhance the discovery process in pharmaceutical industry. The technique is based on
thermophoresis, the directed motion of molecules in temperature gradients. This thermophoretic
movement is affected by the entropy of the hydration shell around molecules and is highly
sensitive to binding and oligomerization reactions, which affect the size, charge, conformation or
hydration shell. Furthermore, MST assays are highly adaptable to fit to the diverse requirements
of different biomolecules, e.g. membrane proteins to be stabilized in solution. The type of buffer
and additives can be chosen freely. Measuring is even possible in complex bioliquids like cell
lysate and thus under close to in vivo conditions and without sample purification.
Since this technology is not limited by any changes in size upon binding, even very small
compounds and fragments can be investigated for binding to their target molecule. The MST
technology allows for the determination of binding affinities and other biophysical parameters
such as stoichiometry directly in solution without surface immobilization. Exploiting the intrinsic
tryptophan fluorescence of proteins this method provides a truly label-free experimental setup.
This combination of high sensitivity towards small molecules and close to native conditions in an
immobilization-free and label-free experimental design makes MST a powerful method for drug
discovery. A combination of different biophysical techniques should be employed to shed light
on different aspects of their mode of action, thus improving the quality of therapeutics and speed
up the development process.