Risk & Reporting
measures drafted over the last few years require banks to focus
on improving transparency, ensuring accountability and implementing warning
systems. These requirements are largely internal but can indirectly a¥ect
resources and operations. Regulators have recently been forcing multinational
financial institutions to set up subsidiaries and separate riskier operations
from basic banking activities. Such restructuring is a dicult task from an
operational standpoint and is often associated with increased manpower
and real estate costs.
Governance, Organization & Reforms
are measures to strengthen
regulatory oversight. They include consumer protection rules,
enforcement of shadow banking controls, reforms to credit rating
agencies and derivatives markets, etc. The multitude of reforms
imposed upon banks significantly impacts their business models
and baseline profitability.
Trimming the fat in Asia
Regulatory constraints have hit banks hard following the
financial crisis, adding to the impact of uncertain market
conditions. Fines and litigation due to regulatory lapses,
rising capital requirements, the steep increase in
funding costs due to Basel III bu¥er norms, slower
economic growth and lower-than-expected returns
have all pushed major global banks in the Asia
Pacific region to embark on a cost containment
¿ Thomson Reuters, State of Regulatory Reform 2016. Deloitte,
Top regulatory trends for 2016 in Banking. KPMG, Evolving
Banking Regulation, March 2015. CDW financial services, Tech
trends for banks, 2015 & 2014. Unwork & DTZ, The future of the
financial workplace, September 2014.Goldman Sachs, Who pays for
bank regulation? June 2014. Cushman & Wakefield Research.
2/3
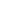
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE REMAINS A PRIORITY
1
NEARLY
MORE THAN
of global financial services
companies are feeling
significant impacts from
regulatory reforms
60%
of global financial services
companies improved
infrastructure to support
growing scrutiny
17