Straight Thermocouple Assemblies
-
Mountings and
Attachments
l.i::,ir.:t1.,:',)::;1lr{
11...,.;t
tl!,;.
t
;,,
. ,i:,:
::l,i
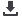
Adjustable
Flanges
A
adjustable flange
is
used to adjust the protection tubes depth
of
insertion.
ln
most cases the tube should extend into fluids
at
least
six
times the outside
diameter
of the
tube.
lf
the tube
is going
into
a gas,
it
should extend
a
minimum of eight times the outside
diameter
of the tube.
The adjustable llange can also
be
used
to
extend the connection head away from excessive heat or corrosive
gases.
A
flange will not give
a
gas
tiglrt
seal.
f
a
gas
ilght
seal
is
required, a threaded
(IF)
or welded fitting
W)
should
be
used.
On
ceramic
tubes
it is
necessary
to
have
a
metal
sleeve
to
mount
the tlange. This will prevent
the
tube from breaking when the set
screw
is
tightened.
This sleeve
is
normally made
from
high
temperature #9 alloy (600).
To
add a adjustable flange
to
a
mekl
or
ceramic
assembly, add
AF
to the
end
of
the
paft
number.
Examples:
MeIal 8K4-722-1S-AF
(18"
#7
alloy metal tube assembly, and
a
adjustable flange)
Ceramic-
8K4-P11N9A6-18-AF
(18" mullite tube assembly, and
a
adjustable flange)
Extensions
A
extension may
be
used where it
is
not necessary
to
have
the alloy
pipe exend
through the cool part of the
furnace.
By using a steel
extension, the total cost of the protection tube can
be reduced.
The extension
also
keeps the connection head out of
any
corrosive
gases
and
away from excessive
heat.
Extensions can be
added to
metal or
ceramic
protection tubes.
To
add a extension
to
a metal
or
ceramic
assembly,
add
E
and
the
number
of
inches
of
ertension
to the
end
of
the
parl number
Examfles:
Metal- 8K4-722-18-E-1
2
(1
B"
#7
alloy metal tube assembly, and
a
1
2"
extension)
Ceramic-
8K4-P11F-18-E-12
(18" mullite tube assembly,
and
a
12" extension)
Tlrreaded
Fittings
A threaded fitting is screwed
on
to the open end of
a
protection tube and then screwed into
the
furnace to give
a
gas tight
seal.
The third
thread permits the tube
to
be extended beyond the fitting for mounting a terminal
head.
The replacement of
a
protection tube with
a
threaded
fitting is
less
epensive
than one with a
welded
bushing since
only
the tube has to be
changed.
The standard outside thread size of a threaded
fittingisl l/4"NPT
1/2"NPTthreadedfittingsarestandardoutsidethreadsonl/4"andl/8"pipesizes.
Othersizescanbeorderedby
specifying the size in 1/16ths of an
inch.
Example:
A 1
112"
x1/2"
x112" threaded fitting would
be a
F2408.
To
add a
threaded
fifting
to
a
medl
assembly,
add TF
to
the
paft
number.
Examfle:
Metal-
8K4-722-18-TF-O
(1
8" #7
alloy metal tube assembly, threaded fitting, and
a 6"
nipple)
Welded
Fittings
A
welded fitting is welded directly on the the protection
tube.
The tube
than
can be screwed into the furnace to give
a
gas tight seal.
Protection tubes with a welded fitting
are
more
epensive
than
threaded fittings since the alloy extends outside
the
furnace.
Also the fitting must be
replaced with the
tube.
The standard outside thread size on a welded fitting
is 1
114"
NPT
1/2" NPT outside thread welded fittings are standard
on
1/4"
and
1/8"
pipe
sizes.
Other sizes can be
ordered
by specifying the
size
in 1/16ths of an
inch.
',lexample:
A1
112"
x112"
xl12"
welded fitting would
be
a W2408.
To
add
a
velded fitting
to
a metal
assembly,
add
W
follofied by
the
immersion length
(
-*)
to the
paft
number.
Example:
Metal-
8K4-734XH€6-W-24
(36"
#7
alloy metal tube assembly,
1
1/4" welded fitting,
24"
immersion
length
measured from the
tip of
the tube to the bottom of the
fitting)
The immersion length is shown
as
(U)
on ligure
4.
ln
most
cases
the tube should extend
into
fluids at least six
times
the outside diameter of
the
tube.
lf
the tube is
going
into
a
gas, it should extend
a
minimum of eight times the outside diameter of the tube.
Page 30