Latest News
SolarEdge Technologies, Inc. (“SolarEdge”), a global
leader in smart energy technology, announced the closing
of the previously announced acquisition of a majority
stake (approximately 56%) of S.M.R.E. Spa (“SMRE”), a
provider of innovative integrated powertrain technology
and electronics for electric vehicles.
“We are pleased to welcome SMRE to the SolarEdge family.
We believe that our technological synergies combined
with our complimentary areas of expertise will empower
SolarEdge’s growing business group at a time when the
world is undergoing a clean energy transformation and
e-mobility revolution,” stated Guy Sella, CEO, Chairman
SolarEdge Announces Closing of S.M.R.E. Spa Acquisition
and Founder of SolarEdge.
The Company’s current aggregate investment to purchase
the SMRE shares was increased from 51% to 56% totaling
approximately $85 million, up from the expected $77
million, including transaction-related expenses. SolarEdge
intends to purchase the remaining outstanding equity
shares of SMRE that are currently listed on the Italian
AIM
(SMR.MI) over time through open-market purchases
and otherwise, eventually resulting in SMRE becoming a
wholly-owned subsidiary of SolarEdge.
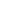
Smart microrobots that can adapt to their surroundings
Scientists at EPFL and ETH
Zurich
have
developed
tiny elastic robots that can
change shape depending on
their surroundings. Modeled
after bacteria and fully
biocompatible, these robots
optimize their movements so
as to get to hard-to-reach areas
of the human body. They stand
to revolutionize targeted drug
delivery.
One day we may be able to ingest tiny robots that deliver
drugs directly to diseased tissue, thanks to research being
carried out at EPFL and ETH Zurich.
The group of scientists – led by Selman Sakar at EPFL
and Bradley Nelson at ETH Zurich – drew inspiration from
bacteria to design smart, biocompatible microrobots that
are highly flexible. Because these devices are able to
swim through fluids and modify their shape when needed,
they can pass through narrow blood vessels and intricate
systems without compromising on speed or maneuverability.
They are made of hydrogel nanocomposites that contain
magnetic nanoparticles allowing them to be controlled via an
electromagnetic field.
In an article appearing in Science Advances, the scientists
describe the method they have developed for “programming”
the robot’s shape so that it can easily travel through fluids
that are dense, viscous or moving at rapid speeds.
Embodied intelligence
When we think of robots,
we generally think of bulky
machines
equipped
with
complex systems of electronics,
sensors, batteries and actuators.
But on a microscopic scale,
robots are entirely different.
Fabricating miniaturized robots
presents a host of challenges,
which the scientists addressed
using an origami-based folding method. Their novel
locomotion strategy employs embodied intelligence, which
is an alternative to the classical computation paradigm that
is performed by embedded electronic systems. “Our robots
have a special composition and structure that allow them
to adapt to the characteristics of the fluid they are moving
through. For instance, if they encounter a change in viscosity
or osmotic concentration, they modify their shape to maintain
their speed and maneuverability without losing control of the
direction of motion,” says Sakar.
These deformations can be “programmed” in advance so as
to maximize performance without the use of cumbersome
sensors or actuators. The robots can be either controlled
using an electromagnetic field or left to navigate on their
own through cavities by utilizing fluid flow. Either way, they
will automatically morph into the most efficient shape.
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 13