EuroWire – January 2012
81
Technical article
High speed laser gauges for
lay length measurement and
FFT analysis for assessment
of process stability
By Stephen Pearson, Tyco Electronics, Greensboro and Kenneth E Cornelison, Beta LaserMike, Dayton
Abstract
In this paper, we describe the work
done to evaluate crosstalk performance
in
Category
5
and
higher
data
communication cables. Specifically, a new
technology was introduced that allows the
accurate measurement of the lay of pairs.
In addition this technology provides
information about the variability of the
lay along the length of the pair. We show
in this paper how the pair lay length as
well as the variation of the lay affect the
crosstalk performance.
Unlike designs that intentionally induce
changes in lay length, the effects
discovered and described occur as part of
the mechanical operation of the pairing
and cabling equipment.
We have shown that by changing set
points on the machines other than the
lay setting itself, changes in the crosstalk
performance of finished category cable
performance occurs.
These changes in performance are also
accompanied by changes in the lay length
values, even with the same lay length set
points on the machine.
1 Introduction
It is well known in the industry that
crosstalk is a key characteristic for high
performance category cables.
In
many
instances,
manufacturers
guarantee crosstalk performance better
than industry standards. This high level of
performance requires the implementation
of a solid product design and stable
manufacturing processes. It is also well
known that even with a solid design,
excessive process variation will reduce
crosstalk
performance.
Changes
in
performance may occur quickly in the case
of a specific machine or process upset.
Changes in performance may also occur
slowly over the course of days or weeks
that are often caused by gradual changes
in the operation of the manufacturing
equipment.
It is not uncommon to implement
scheduled maintenance of equipment
to reduce the instances of performance
degradation, but the effectiveness of that
maintenance to control the lay length
attributes has not been understood
adequately.
Another key factor affecting crosstalk
performance is the consistency of lay
lengths across a number of different
machines. It is known, or at least
previously suspected, that the lay length
can be different from machine to machine.
Managing the use of different machines
on a factory floor without good feedback
on the actual pair lays is often a problem.
This can also be a significant barrier to
production scheduling, since often only
certain ‘qualified’ equipment can be used
on specific products.
A new lay length measurement tech-
nology has been developed that allows
high speed acquisition of lay length data.
With this technology, lay lengths can
be accurately measured across different
machines.
This information can be useful in a number
of ways. For instance, each machine on a
production floor could then be adjusted to
deliver a single desired lay value.
The variation around the nominal lay is
also an important factor that contributes
to the crosstalk of the completed cable. We
show that effects such as the double twist
bow rotation as well as the pretwist of the
single wires are quite visible in the analysis
of pair length variation.
In some cases, even variation caused by
the rotation of the payoff and take up
spool can be seen in the pair lay data.
▲
▲
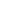
Figure 1
:
Example of lay length distribution
Frequency
% Deviation fromTarget
Pair 1
% Dev Pair 1