Acknowledgement
This article is based on extracts taken from IAEA TECDOC
No. 1744, IAEA, Vienna (2014): International Atomic
Energy Agency, “Treatment of Radioactive Gaseous
Waste” and is published here with the kind permission
of the IAEA. For the complete publication, please see
http://www-pub.iaea.org/books/IAEABooks/10741/Treatment-of-Radioactive-Gaseous-Waste. © IAEA
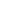
Table 4: A selection of treatment methods for gaseous and
airborne waste.
• Building supply and extract systems.
The principle species to be treated in the THORP off-gas
system are 129I, -C, NOx, fuel dust particles and aerosols
containing plutonium and/or mixed fission products. THORP
is designed on the principle of cascading depressions
between areas to provide barriers against the spread of
contamination. The main ventilation streams are kept
separate until they enter the 125 m stack from which they
are discharged into the atmosphere.
The prime task of the dissolver off-gas (DOG) system is to
remove nitrogen oxides (NOx) generated by the dissolution
of the UO
2
fuel, together with the major volatile radioac-
tive species released as the fuel is dissolved. The off-gas
streams from different parts of the plant or from different
types of equipment are combined into a series of “headers”,
which feed into the COG system at an appropriate point ac-
cording to the type of decontamination required.
Overview of technology options
Table 4 gives a selection of treatment methods for gaseous
and airborne waste [29].
Information and data on the components and elements of
air cleaning and gas processing systems are the subject
WASTE MANAGEMENT
of a separate report. In addition to that the report covers:
• Fibrous filters, medium and high efficiency;
• Granular bed and sand filters;
• Iodine adsorbents;
• Modular iodine adsorbers;
• Monolithic iodine adsorbers;
• Mist eliminators, coalescers, etc.;
• Scrubbers and condensers;
13
Chemical Technology • October 2016
Treatment
Method
Features
Limitations
Secondary
Waste
HEPA
High efficiency
particulate
filtration
Glass Fibre filter media,
high efficiency 99,97%,
widespread use,
retention of sub-micron
particles 0.3µ
Humidity control and
prefilters required to
protect HEPA filters
HEPA and
prefilters
Sorption
Chemically impregnated
charcoal or zeolites
to remove inorganic
and organic iodine in
reactors.
Humidity control and
charcoal has limited
operating temperature.
High cost.
Spent media
Cryogenic
Trapping
Kr in offgases adsorbed
on solid sorbent like
charcoal. Operates at
elevated pressure and
reduced temperature. Kr
can be recovered and
sorbent used multiple
times.
Further processing for
storage is required.
Commercial experience
limited.
Spent
sorption
media
Delay / Decay
Used for decay of short
lived noble gases
Large beds for retention
time required
None
Wet Scrubbing
Scrubbing solution
targets compounds
and particulate matter.
Used for process
offgas treatment. Can
be as simple as water
or reagents targeting
specific compounds
Not practical for high
volume gaseous stream
treatment
Liquid waste
streams
• Cyclones;
• Electrostatic precipitators;
• Recombiners (H
2
-O
2
) and (NO
x
-NH
3
);
• Other considerations (fans, stacks, etc);
• System testing;
• New technologies.
References
References for this article are available from the editor,
Glynnis Koch, at
chemtech@crown.co.za