6-4
Chapter 6
- Service Tools & Their Use
Go to Chapter Start-
Table of Contents-
IndexThese special hoses and fittings are designed to minimize refrigerant loss
and to preclude putting the wrong refrigerant in a system.
Two hoses (left and right) connect to the low and high sides of the
system, usually at the compressor on R-12 systems. The center (utility)
hose is used to remove refrigerant from the system, evacuate air and
moisture, or add refrigerant. Gauges are calibrated for either high or low
pressure and vacuum. The term compound gauge set is often used be-
cause the low pressure gauge responds to pressure and vacuum. Separate
gauge sets are required for R-12 and R-134a.
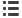
0
100
200 300
400
500
HIGH
TEMPERATURE
LOW
TEMPERATURE
150
120
90
60
30
0
10
20
30
LOW SIDE (SUCTION PRESSURE)
HIGH SIDE (DISCHARGE PRESSURE)
VALVE CLOSED
LOW SIDE
HAND VALVE
TURN CLOCKWISE TO CLOSE
SERVICE HOSE & FITTING TO LOW SIDE
UTILITY HOSE AND FITTING (FOR SYSTEM SERVICE)
SERVICE HOSE & FITTING TO HIGH SIDE
TURN COUNTER CLOCKWISE
TO OPEN
HIGH SIDE
HAND VALVE
VALVE OPEN
CAUTION
Many gauges have dials with metric and US scales to
measure pressure. The more expensive manifold
gauge sets have liquid filled gauges and additional
valves and fittings incorporated in the manifold. All
gauges are breakable and should be handled with a
reasonable amount of care.
The high pressure gauge registers system pressure from 0 to 500 PSI. The
low pressure gauge registers pressure from 0 to 150 PSI clockwise, and
vacuum from 0 to 30 inches Hg counter-clockwise.
There are a few important rules and procedures you must follow
concerning gauge set hookup. Both the rules and procedure are for your
safety and to protect the AC system. The basic rules are covered briefly
here. Gauge set hookup should not be done until after you have made a
complete visual and performance inspection of all AC system components.
These inspections are described in detail in
Chapter 7
. In addition you
should inspect the engine, cooling system and other engine driven de-
vices. Engine cooling system problems can cause false gauge readings and
incorrect AC system diagnosis. Worn drive belts or hoses are dangerous to
work around.
Figure 6-2
The basic manifold and
gauges are illustrated. The
low pressure gauge displays
pounds per square inch
(PSI) and inches of mercury
(in. Hg). Hg is the chemical
symbol for mercury. The
high pressure gauge reads
in pounds per square inch.