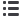
The method … is ready
I have GxM equations of the form (1) @ each
voxel (GxMxN
vox
in total)
•
begin with E1 (highest energy group)
)5(
) ( ) ,(
1
)( ,
)4(
) ˆ(
) (
1
)( ,
1
)(
,
,
)3(
'
)' ( )
,(,
1 1'
'
)(
' ,,
)2(
0
) ,(
1'
)(
' , ,
)(
' ,,
)ˆ,( , ,
)1(
)
(
1 4
, ,
, ,
)( ,
,
)( ,
ˆ
dEEfErt
gE
gE
rgt
dEnwn
m
l
YEf
N
n
rng
g
E
gE
r
gm
l
dEdE EfE Erls
gE
gE
gE
gE
rg
gls
l
l
l m
m
l
Y
G
g
r
gml
rg gls
rng scat
q
pr r
P
p
ngpq
ng scat q rng gt
rng
−
=
=
−
=
→
−
−
= −
=
−=
=
−
=
−
=
+
=
+
0
)(
,1
=
iter
r
n
•
make an initial guess for
•
calculate cross sections from (3) & (5)
•
calculate the expansion from (4)
•
use these in (2) to calculate q
scat,1,n
•
solve (1) for
1 )
( ,1
=
iter rn
•
if convergence criterion met, proceed with g=2
BUT…:
1. I need to be efficient
(t~ GxMxN
vox
x#iters.x order of legendre exp.)
& work
with finite voxels
2. I need to account for inhomogeneities
3. I need to work with real sources
4. I need to account for finite patient dimensions
•
if convergence criterion not met, re-iterate