with several different types of sensors
which use both standard and bespoke
interfaces.
Users also benefit from the most
efficient processing power per
watt, where these applications are
often battery powered this enables
the application to last longer on its
batteries and hence achieve more.
They can also leverage the power
management features of the all
programmable systemon chip devices
to scale the power consumption in line
with the demands of the operating
conditions, for example, detecting that
a smart augmented reality headset is
no longer being worn and entering a
sleep mode to conserve battery life.
Both All Programmable SoC and
FPGA also provide inherent security
features such as secure configuration
and the ability to monitor internal
voltages and temperatures to detect
unauthorized access attempts to the
device.
Finally, they must also consider the
future upgrade path and the need to
support new standards, frameworks
and interfaces as these are released.
The use of programmable logic
provides for a product technology
roadmap which can easily scale due
to its any to any interfacing capability.
Conclusion
As demonstrated, image processing
is ubiquitous with applications both
at the edge and the cloud, facing
many of the same challenges.
The use of acceleration stack
based approaches which support
development of image processing
systems in both applications enables
the system developer to leverage
both the system and performance
benefits which come with the use of
programmable logic.
Both stacks presented are also
very flexible and will be developed
over time to add support for new
frameworks and standards as they
are introduced.
image processing algorithms
within the programmable logic.
Compared to implementing the same
function within a processor based
architecture, RAS provides a 40 times
improvement when implementing
image processing algorithms and 11
times when performing deep machine
learning. While using the reVISION
stack provides between 40 and 400
times acceleration depending upon
the algorithm and SoC selected.
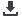
These significant performance
improvements provided by RAS within
the cloud enable not only a reduced
hardware requirement to achieve the
same performance, but also provide
for a lower cost of ownership and
operation as the power consumption
is also significantly reduced. The
cloud can also take advantage of
the reconfigurable nature of FPGA’s
at run time and re configure the
programmable logic for different
algorithms as they are called to be
executed.
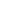
Using the reVISION stack at the edge
not only do they obtain the same
performance increase but again they
are also able to leverage the any to
any interfacing capability provided
by the programmable logic. This is
especially important in edge based
solutions where they must interface
Fig 3 - Reconfigurable Acceleration Stack
Fig. 4 -reVISION Stack
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 29