SOCIAL, ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIETAL RESPONSIBILITY
A3
2. Environmental information
Through its specialists and their networks, the department disseminates information
related to accomplishments, best practices and events in order to prevent risk and
promote performance improvement.
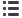
NUMBER OF EVENTS IN THE GROUP IN 2016 RANKED
ON THE INES
(1)
SCALE, EITHER IN THE NUCLEAR ENTITIES
(OWNER-OPERATORS, CONTRACT OPERATORS,
SERVICE PROVIDERS) OR DURING THE SHIPMENT
OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS
Level 0
Level 1
Level 2
2013
2014
2015
2016
154
137
157
143
19
19
19
17
0
0
0
0
Source:AREVA.
Health, Safety and Environment training
AREVA’s Safety Excellence program, a professional development program for
managers with operational delegation of authority, was established in 2012 and
has gradually been expanded. The program is based in particular on assessments
of skills in nuclear safety, radiation protection, materials transportation, materials
safeguards, industrial safety, protection of nature and the environment, and
occupational health and safety, and on a body of mandatory training programs.
It is intended for site directors; duty officers; facility managers; health, safety and
environment managers (HSE); and project managers at AREVA’s industrial sites.
For site directors, the program includes a module devoted to HSE management.
Twelve site directors and production managers with delegation of authority took
this module in 2016 in connection with new duties or to maintain their skills. A total
of approximately 130 site directors have taken the program since its establishment.
A Health, Safety and Environment training program is offered to facility managers; it
consists of two modules and work in small groups on operating practices. Starting
in 2014, the program was made mandatory for new facility managers. Forty-two
facility managers took the program in 2016.
In addition to the training required by regulation and training programs on risk
and safety culture given at the operator and site level, the group has defined and
offers training programs on nuclear safety, human and organizational factors (HOF),
significant event analysis, and occupational safety for target groups.
Employee information
AREVA communicates regularly with its employees on HSE subjects to give them
information on policies, applicable benchmark documents, the sharing of best
practices from operating experience, and risk prevention actions. This information
is communicated via email and on the AREVA intranet, and through regular network
information meetings.
Information on AREVA’s commitments in favor of the circular
economy
A defining feature of AREVA is its development of a pioneering, competitive position
in the circular economy through its fuel cycle operations. Its industrial tools in the
back end of the cycle enable it to recycle energy recovered from the plutonium
contained in used nuclear fuel into fresh MOX fuel. Some 96% of the content of
“used” nuclear fuel is recoverable. These materials are extracted at the AREVA
NC la Hague site and used in the MOX fabrication process (mixed oxide fuel) at
the MELOX plant site to resupply reactors. Such recycling limits our consumption
of natural uranium.
Industrial know-how on this scale is unique in the world. It significantly reduces
environmental impacts across the entire uranium lifecycle, in particular during the
mining stage, which has the biggest impact in terms of footprint.
In addition, the group has always aligned its internal practices with these issues in
order to very significantly and proactively reduce its environmental footprint across
the entire nuclear fuel cycle.
For example, from the early days of its establishment, AREVA has built an internal
system of environmental performance indicators to measure the results produced
by changes in individual behavior, the optimization of existing facilities, or major
technological leaps.
This sense of responsibility was further encouraged for five years by an internal
market for offsets to carbon-emitting activities, with the operating entities financially
encouraged to pursue eco-design efforts in favor of cleaner technology solutions.
From the start, AREVA ensured that the results of this initiative were indisputable
by coming up with auditable performance indicators. For example, AREVA’s “non-
financial reporting system” has been audited each year since 2004 by the statutory
auditors, and the results are published in the Group’s annual report.
At the end of 2014, a ten-year assessment indicated a 66% reduction in greenhouse
gas emissions at constant revenue, an 89% reduction in energy consumption, a
91% reduction in water consumption, and a 48% reduction in unrecycled waste.
Some of the programs showcasing waste recovery and reuse include:
p
waste recycling from the metal segment of the zirconium operations into raw
materials used in the production of nuclear-grade zirconium sponge;
p
recycling in offsite foundries of chips produced by the manufacturing of large
forged and cast parts at AREVA NP’s Creusot site and their reintroduction into
the head end of the process;
p
recovery at the AREVA NC Malvési site of potassium diuranate produced by the
uranium ore conversion operations of the AREVA NC Pierrelatte site.
(1) International Nuclear Event Scale.
344
2016 AREVA
REFERENCE DOCUMENT