BUSINESS OVERVIEW
06
6.4 Operations
6.4.2.1.1.
Fuel
Businesses
The Fuel business designs, fabricates and markets fuel assemblies and provides
fuel-related services for power generating stations with light water reactors
(commonly called PWR for pressurized water reactors and BWR for boiling water
reactors). In addition to conventional enriched natural uranium oxide fuel (UO
2
), the
Fuel business markets MOX fuel (a mixture of uranium and plutonium oxides) and
enriched recycled uranium fuel (ERU – see
Glossary
) containing fissile materials
from the used fuel recycling process. MOX fuel fabrication is provided by the
Recycling business (see Section 6.4.1.3.1.
Recycling
).
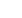
PRINCIPAL STAGES IN FUEL ASSEMBLY FABRICATION FOR LIGHT
WATER REACTORS
Upper rod assembly
Top nozzle
Guide thimble
Mixing grid
Fuel rod
Bottom nozzle
Fuel
assembly
Reconversion
Components
Skeleton
Rods
Guide
thimbles
Cladding
Rod fabrication
Pellets
UF
6
UF
6
into UO
2
of enriched
Grids
Nozzles
Enriched
Source:AREVA, PWR reactor system.
Reactor safety is a function of several requirements:
p
containment, in the nuclear safety sense, of radioactive products under both
normal and accidental operating conditions;
p
control of the chain reaction; and
p
cooling of the reactor core.
Fuel assemblies contribute to reactor safety by sealing fissile materials and
radioactive fission products inside zirconiumalloy cladding, which forms the primary
containment barrier.
Once unloaded from the reactor, the fuel assembly must continue to provide
containment of the fissile materials and fission products, allow for residual heat
dissipation and fuel handling, even after having been stored for relatively long
periods, and allow for treatment when the closed fuel cycle has been chosen. The
number of assemblies periodically replaced simultaneously (every 12 to 24months)
constitutes a fuel reload.
The Fuel business has expertise in every aspect of the fuel design and fabrication
process, from the production of zirconium and its alloys to fabrication of the final
fuel assembly. A large number of high-level scientific and technical skills must be
brought together to achieve flawless design and fabrication quality, an absolute
requirement. The Fuel business has three major areas of expertise:
p
fuel design: This brings into play neutronic, thermohydraulic and mechanical
design codes and databases built on lessons learned frommany years of reactor
operations. Fuel designs are referenced in reactor operating license applications,
making the fuel designer one of the utility’smost important partners in its relations
with its national or local safety authority;
p
zirconium and zirconium alloy production: This draws on expertise in chemical
and metallurgical processes and technologies;
p
fuel assembly fabrication: This requires knowledge of chemistry; powder
metallurgy; various assembly techniques, including advanced welding,
mechanical systems andmachining; and numerous methods for non-destructive
examination and physico-chemical analysis.
The Fuel business also manufactures zirconium-based products and semi-
finished products which may be sold, including to some competing fuel assembly
fabricators. In addition, the Fuel Business Unit markets fuel-related engineering
services, fabrication services and onsite services.
Operations and highlights
The streamlining and performance improvement of the production plants continued:
p
in Dessel, Belgium, the last fissile material present at the site was transferred
to other sites of the group, and site dismantling continued towards the goal of
completion in 2018;
p
in France, the transfer of themanufacturing of spacer grids and rod cluster control
assemblies from the Pierrelatte site to the Romans plant began, with completion
scheduled in 2017. Lastly, construction of the new emergency command center
at the Romans plant in France was completed, in accordance with its safety
commitments.
Concerning the zirconium operations, a furnace exploded in the melting facility of
the Ugine plant in France, with no injuries or environmental impacts but with an
impact on 2016 production volumes. Elsewhere, the CAST joint venture in China
with SGTC (a subsidiary of the Chinese nuclear group CNNC) continued to deliver
cladding tubes to CJNF, also a subsidiary of CNNC, in China.
Human and industrial resources
The Fuel business is structured into several entities with facilities in Europe and
the United States:
p
the Products and Technologies; Fuel Design; Sales, Contracts and Services;
and Supply Chain Divisions;
p
the Components Operations Department, which includes all of themanufacturing
processes for zirconiumproducts, from zircon ore to the finished products. It has
five plants in France, each specialized in one aspect of zirconium metallurgy or
forming, and two joint ventures, one in Japan and the other in China;
p
the Fuel Operations Department organized into five production sites, one in the
United States and four in Europe, whichmainly supply US and European utilities.
In Japan, a joint-venture production site serves the Japanese market;
p
Cerca’s operations in France, whichmainly involve the fabrication and sale of fuel
elements for research reactors and of fuel targets made with enriched uranium.
6.4.2.1.
NEW NP OPERATIONS
2016 AREVA
REFERENCE DOCUMENT
81