69
• Key performance indicators: As documents of evidence, key performance
indicators can also be used to prove compliance with certain criteria. In
addition to that, they may also represent criteria of their own. Here, a
criterion could be defined that organisations use KPIs in their planning and
control process or the actual value of a certain KPI is evaluated. Industry
associations provide a set of KPIs such as share of purchasing cost, cost per
order or spend under management for the purchasing function. Also the
provided benchmark values allow a quick evaluation of the assessed unit.
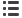
An example of the content dimension is the design of the specific criterion “data
transparency”. It summarises the results of the structure and the content of an assessment
model. It is presented in Figure 3.15 and afterwards shortly discussed.
Figure 3.15 Example criterion data transparency
Data transparency is the basis for a good and consistent development of a material
and supplier strategy as well as for some operational decisions and therefore a very
important criterion in strategic procurement. The evaluation logic is based on four
levels. The best-practice can be seen in the “Excellence”-level, which could have been
defined by internal benchmarking or market research. It is important for multinational
companies that there is a certain consistency in the data transparency in every purchasing
and procurement unit. Therefore, this criterion should be used in the assessment of every
unit and should be weighted relatively high. Also the goal should be that every assessed unit
should achieve at least the “Established”-level (which is not evident for plant purchasing
units that were newly acquired and in developing countries). Documents of evidence to
prove the level are available reports (optimally extracted from the ERP – or procurement-
system as information source). KPIs to double-check this criterion could be the analysis
of the spend under management (as it is very difficult to manage the spend actively when
there is no data basis available), the development of the cost per order (as an excellent
usage of IT-tools imply that the automation rate is high) or the realised savings (as a good
data transparency is the basis for an intelligent management of the TCO).
The assessment method describes the process how a maturity assessment is conducted.
It covers aspects such as the involved parties, the assessment process and its related
activities and tool-support:
• Stakeholder: Typical stakeholders in maturity assessments for procurement
include the principal (e.g. the Group-CPO, C-level managers of the business
unit or the leader of the assessed procurement unit), the assessed unit, the
assessors themselves and possible cross-functional partners of the purchasing
organisation such as the production department, business development or the
accounting department. It is crucial to integrate the stakeholders in the model-
building process to cover their needs.When, for example, the assessment should