observer when a PGY-2 or higher-level resident
delivered the handoff, compared with PGY-1 resi-
dents (mean of 4.3 vs 3.6,
P
<
.001). The receiver
scores did not show a difference based on the
source PGY resident level (
P
= .56).
ICC was used to compare different participants
of the study. Observers 1 and 2 were found to have
a strong ICC when counting distractions and
evaluating the handoff delivery process and hand-
off environment (
P
<
.05). In contrast, the 2 ob-
servers diverged when evaluating the handoff
reception process (
P
>
.05;
Table IV
). Also, the 2
receivers diverged in evaluating the type of
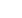
Fig 2.
Time per patient handoff as a function of the number of patients being handed off. (Color version of this figure
is available online.)
Table III.
Distraction categories noticed by source
and receivers
Source Receiver 1 Receiver 2
Any distraction
71 78
67
Internal noise (% yes)
56 71
62
Hunger (% yes)
26 22
23
Void (% yes)
6
4
0
Thirst (% yes)
17 17
15
Pain (% yes)
1
5
0
Fatigue (% yes)
37 60
28
Other (% yes)
1
1.2
0
Personal distractions
(% yes)
12 12.2
18
External noise (% yes)
39 44
41
Extraneous staff
entering/exiting
the room (% yes)
28 31
15
Background conversation
by extraneous
staff (% yes)
5 17
3
Side conversations by
handoff staff (% yes)
6
2
3
Teaching discussion
during handoff (% yes)
4
4
0
Unrelated electronics
on during handoff
(% yes)
10
9
28
Table IV.
Observer 1 and observer 2 comparison
using ICC (
N
= 23)
ICC
P
value
Handoff duration (min)
0.983
<
.001
Number of patients per handoff
0.986
<
.001
Number of extraneous staff
entering/exiting room
0.912
<
.001
Background conversation by
extraneous personnel (Y/N)
0.667
<
.001
Number of side conversations
by handoff providers
0.394
.032
Number of handoff interruptions
due to pager beeps/phone
0.765
<
.001
Number of handoff interruptions
due to extraneous staff talking
to handoff staff
0.659
<
.001
Number of unrelated teaching
discussions interrupting handoff
0.209 NS
Were any electronic devices on
during handoff?
0.167 NS
Rate handoff delivery (1–5)
0.556
.001
Rate handoff reception (1–5)
0.062 NS
Rate handoff environment (1–5)
0.447
.016
NS
, Not significant (
P
value
>
.05).
ARTICLE IN PRESS
Hasan
et
al
98