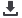
Differential DVH of “ideal point source”
The values of the differential DVH for an ideal point source can be calculated
directly because the isodose surfaces are spheres with the source as center,
The Natural Dose Volume Histogram (NDVH)
of which the volumes are easily calculated: V = (4/3)
π
r
3
.
For an ideal point
source with D = S / r
2
, V can be written as a function of D:
V = (4/3)
π
S
3/2
D
–3/2
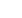
Then, analytically the differential DVH for an ideal point source with D = S / r
2
is given by:
dV / dD = –2
π
S
3/2
D
–5/2
It is then clear that, as the dose decreases, dV / dD increases more than
quadratically.