
Chapter 2
•
Cardiovascular Care
23
PERIPHERAL
ARTERIOGRAPHY
A peripheral angiogram is a test
that uses x-rays and dye to identify
narrowed or blocked areas in one or
more of the arteries that supply blood
to the legs. The test is also called a
peripheral arteriogram.
The angiogram helps determine
if a surgical procedure is needed to
open the blocked arteries. Peripheral
angioplasty uses a balloon catheter
to open the blocked artery from the
inside. A stent, a small wire mesh
tube, is generally placed in the artery
after angioplasty to help keep it open.
Bypass surgery is another procedure.
It reroutes blood around the blocked
arteries.
DOPPLER
ULTRASONOGRAPHY
Duplex Doppler ultrasonography
involves the use of high-frequency
sound waves to image vessels and
evaluate blood flow in the major
vessels of the trunk (heart and intra-
abdominal organs) and extremities
(arms and legs) and in the
extracranial cerebrovascular system
(neck). This noninvasive test shows
the speed, direction, and patterns
of blood flow and is used to detect
narrowing or blockages in arteries
and veins.
A handheld transducer directs
high-frequency sound waves to the
artery or vein being tested. The
sound waves strike moving red
blood cells and are reflected back
to the transducer at frequencies
that correspond to blood flow
velocity through the vessel. The
transducer then amplifies the
sound waves to permit direct
listening and graphic recording
of blood flow patterns.
Pulse volume recorder testing
may be performed along with
duplex Doppler ultrasonography to
yield a quantitative recording
of changes in blood pressure in
an extremity.
Normally, venous blood flow
fluctuates with respiration, so
observing changes in sound wave
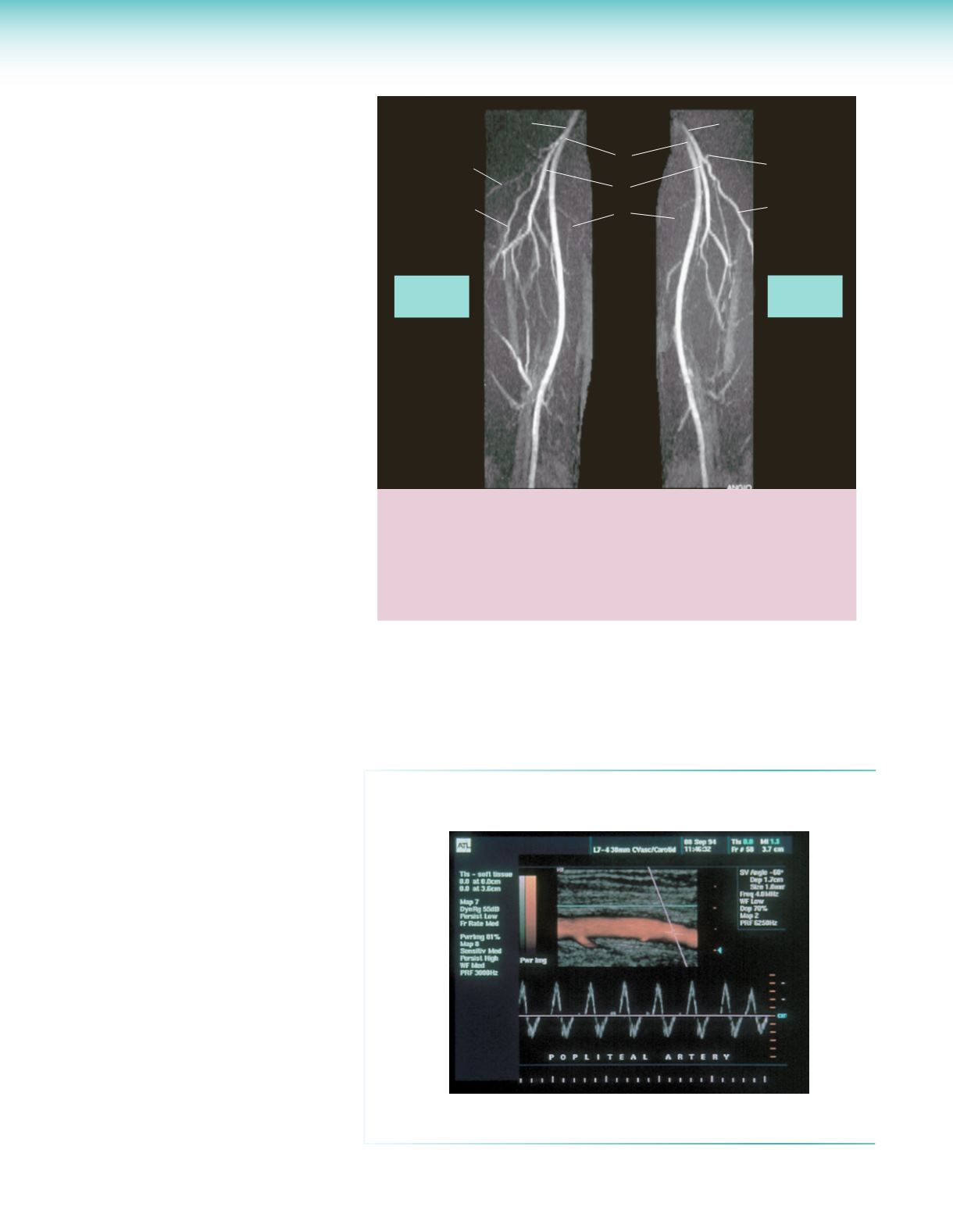
c
a
d
d
c
f
e
b
KEY:
a
= Lateral circumflex femoral artery
b
= Medial circumflex femoral artery
c
= Femoral artery
d
= Descending branch of the profunda femoris artery
e
= Profunda femoris artery
f
= Femoral artery
Patient’s
right leg
Patient’s
left leg
a
Doppler of Popliteal Artery
The image at right shows a color flow duplex image of a popliteal artery
with normal triphasic Doppler signal.
frequency during respiration helps detect venous occlusive disease. Compression
maneuvers can help detect occlusion of the veins as well. Abnormal images and
Doppler signals may indicate plaque, stenosis, occlusion, dissection, aneurysm,
carotid body tumor, arteritis, and venous thrombosis.
Reprinted with permission from Hinkle JL, Cheever KH.
Brunner & Suddarth’s Textbook of
Medical-Surgical Nursing
. 13th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2013.
















